Lemmas | Articles containing proofs | Triangulation (geometry) | Fair division | Combinatorics | Fixed points (mathematics) | Topology
Sperner's lemma
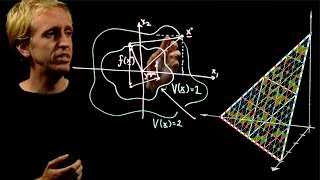
In mathematics, Sperner's lemma is a combinatorial result on colorings of triangulations, analogous to the Brouwer fixed point theorem, which is equivalent to it. It states that every Sperner coloring (described below) of a triangulation of an -dimensional simplex contains a cell whose vertices all have different colors. The initial result of this kind was proved by Emanuel Sperner, in relation with proofs of invariance of domain. Sperner colorings have been used for effective computation of fixed points and in root-finding algorithms, and are applied in fair division (cake cutting) algorithms. Finding a Sperner coloring or equivalently a Brouwer fixed point is now believed to be an intractable computational problem, even in the plane, in the general case. The problem is PPAD-complete, a complexity class invented by Christos Papadimitriou. According to the Soviet Mathematical Encyclopaedia (ed. I.M. Vinogradov), a related 1929 theorem (of Knaster, Borsuk and Mazurkiewicz) had also become known as the Sperner lemma – this point is discussed in the English translation (ed. M. Hazewinkel). It is now commonly known as the Knaster–Kuratowski–Mazurkiewicz lemma. (Wikipedia).