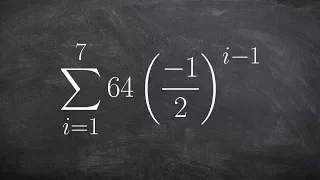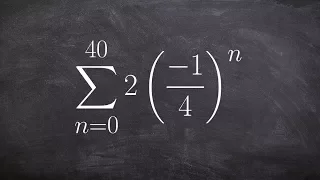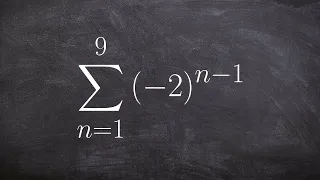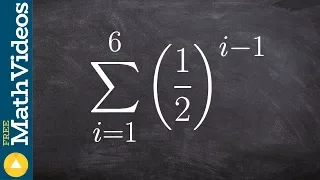Geometric graphs | Random graphs
Random geometric graph
In graph theory, a random geometric graph (RGG) is the mathematically simplest spatial network, namely an undirected graph constructed by randomly placing N nodes in some metric space (according to a specified probability distribution) and connecting two nodes by a link if and only if their distance is in a given range, e.g. smaller than a certain neighborhood radius, r. Random geometric graphs resemble real human social networks in a number of ways. For instance, they spontaneously demonstrate community structure - clusters of nodes with high modularity. Other random graph generation algorithms, such as those generated using the Erdős–Rényi model or Barabási–Albert (BA) model do not create this type of structure. Additionally, random geometric graphs display degree assortativity according to their spatial dimension: "popular" nodes (those with many links) are particularly likely to be linked to other popular nodes. A real-world application of RGGs is the modeling of ad hoc networks. Furthermore they are used to perform benchmarks for (external) graph algorithms. (Wikipedia).