
Theory of numbers: Chevalley-Warning theorem
This lecture is part of an online undergraduate course on the theory of numbers. We prove the Chevalley-Warning theorem, which which gives conditions for a polynomial in several variables to have a solution modulo a prime. For the other lectures in the course see https://www.youtube.
From playlist Theory of numbers

Integral Transforms - Lecture 9: The Fourier Transform in Action. Oxford Maths 2nd Year Lecture
This short course from Sam Howison, all 9 lectures of which we are making available (this is lecture 9), introduces two vital ideas. First, we look at distributions (or generalised functions) and in particular the mathematical representation of a 'point mass' as the Dirac delta function.
From playlist Oxford Mathematics Student Lectures - Integral Transforms

Parseval's theorem is an important result in Fourier analysis that can be used to put guarantees on the accuracy of signal approximation in the Fourier domain. Book Website: http://databookuw.com Book PDF: http://databookuw.com/databook.pdf These lectures follow Chapter 2 from: "Data-D
From playlist Data-Driven Science and Engineering

MIT 8.04 Quantum Physics I, Spring 2016 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/8-04S16 Instructor: Barton Zwiebach License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT 8.04 Quantum Physics I, Spring 2016
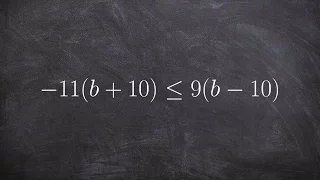
Applying distributive property to solve and graph an inequality
👉 Learn how to solve multi-step linear inequalities having parenthesis. An inequality is a statement in which one value is not equal to the other value. An inequality is linear when the highest exponent in its variable(s) is 1. (i.e. there is no exponent in its variable(s)). A multi-step l
From playlist Solve and Graph Inequalities | Multi-Step With Parenthesis

What is the Riemann Hypothesis?
This video provides a basic introduction to the Riemann Hypothesis based on the the superb book 'Prime Obsession' by John Derbyshire. Along the way I look at convergent and divergent series, Euler's famous solution to the Basel problem, and the Riemann-Zeta function. Analytic continuation
From playlist Mathematics

Lec 20b - Phys 237: Gravitational Waves with Kip Thorne
Watch the rest of the lectures on http://www.cosmolearning.com/courses/overview-of-gravitational-wave-science-400/ Redistributed with permission. This video is taken from a 2002 Caltech on-line course on "Gravitational Waves", organized and designed by Kip S. Thorne, Mihai Bondarescu and
From playlist Caltech: Gravitational Waves with Kip Thorne - CosmoLearning.com Physics
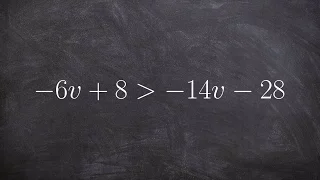
Solving and graphing a linear inequality
👉 Learn how to solve multi-step linear inequalities having no parenthesis. An inequality is a statement in which one value is not equal to the other value. An inequality is linear when the highest exponent in its variable(s) is 1. (i.e. there is no exponent in its variable(s)). A multi-ste
From playlist Solve and Graph Inequalities | Multi-Step Without Parenthesis

Fourier series & Parseval's identity
Free ebook http://tinyurl.com/EngMathYT A tutorial on how to calculate Fourier series and how to derive and use Parseval's identity. Many examples are discussed to illustrate the ideas.
From playlist Engineering Mathematics

Theory of numbers: Gauss's lemma
This lecture is part of an online undergraduate course on the theory of numbers. We describe Gauss's lemma which gives a useful criterion for whether a number n is a quadratic residue of a prime p. We work it out explicitly for n = -1, 2 and 3, and as an application prove some cases of Di
From playlist Theory of numbers

Math 131 Spring 2022 050422 Riesz Fischer; Parseval's theorem
Riesz-Fischer theorem: Fourier Series of a (Riemann integrable) function converge to the original function - in the L2 sense. Consequence: Parseval's theorem: the L2 norm of the function is the l2 norm of its Fourier coefficients.
From playlist Math 131 Spring 2022 Principles of Mathematical Analysis (Rudin)
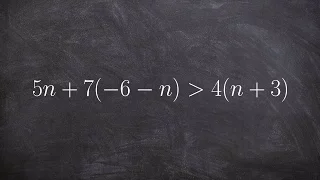
Solving a multi step inequality
👉 Learn how to solve multi-step linear inequalities having parenthesis. An inequality is a statement in which one value is not equal to the other value. An inequality is linear when the highest exponent in its variable(s) is 1. (i.e. there is no exponent in its variable(s)). A multi-step l
From playlist Solve and Graph Inequalities | Multi-Step With Parenthesis
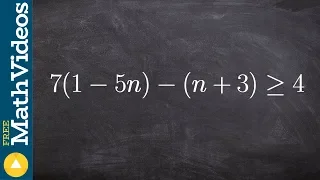
Solving a multi step inequality with double distributive property
👉 Learn how to solve multi-step linear inequalities having parenthesis. An inequality is a statement in which one value is not equal to the other value. An inequality is linear when the highest exponent in its variable(s) is 1. (i.e. there is no exponent in its variable(s)). A multi-step l
From playlist Solve and Graph Inequalities | Multi-Step With Parenthesis

Here we discuss how to compress images using the FFT. Compression is a cornerstone of the modern digital communication era. Book Website: http://databookuw.com Book PDF: http://databookuw.com/databook.pdf These lectures follow Chapter 2 from: "Data-Driven Science and Engineering: Mac
From playlist Data-Driven Science and Engineering

Sum of 1/n^4 (Fourier Series & Parseval's Theorem)
Sum of 1/n^4 by using Fourier Series and Parseval's Theorem, Fourier coefficients from bprp: https://youtu.be/iSw2xFhMRN0 Sum of 1/n^2 from Peyam: https://youtu.be/YMleINbiNlE Sum of 1/n^2 from Max: https://youtu.be/m2o27s1cq8M Sum of 1/n^2 from bprp: https://youtu.be/5-pXwWNcsbc Unfor
From playlist Sum, math for fun
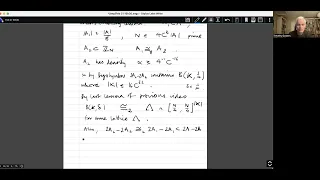
Introduction to additive combinatorics lecture 10.8 --- A weak form of Freiman's theorem
In this short video I explain how the proof of Freiman's theorem for subsets of Z differs from the proof given earlier for subsets of F_p^N. The answer is not very much: the main differences are due to the fact that cyclic groups of prime order do not have lots of subgroups, so one has to
From playlist Introduction to Additive Combinatorics (Cambridge Part III course)

Parseval-Plancherel Identity | Normalization in Quantum Mechanics
In this video, we will investigate the Parseval-Plancherel identity, which is named after the French mathematician Marc-Antoine Parseval, and the Swiss mathematician Michel Plancherel. It states that the integral over the absolute square of a function does not change after a Fourier transf
From playlist Quantum Mechanics, Quantum Field Theory

Solving a multi step inequality with distributive property
👉 Learn how to solve multi-step linear inequalities having parenthesis. An inequality is a statement in which one value is not equal to the other value. An inequality is linear when the highest exponent in its variable(s) is 1. (i.e. there is no exponent in its variable(s)). A multi-step l
From playlist Solve and Graph Inequalities | Multi-Step With Parenthesis

Fourier Series: Example of Parseval's Identity
Differential Equations: Find the Fourier coefficients of the square wave function f(x) = -1 on the interval (-pi, 0), 1 on the interval (0, pi). Then state Parseval's Identity in this case. With this, we show that sum 1/n^2 = pi^2/6.
From playlist Differential Equations

Solving a multi step inequality with distributive property
👉 Learn how to solve multi-step linear inequalities having parenthesis. An inequality is a statement in which one value is not equal to the other value. An inequality is linear when the highest exponent in its variable(s) is 1. (i.e. there is no exponent in its variable(s)). A multi-step l
From playlist Solve and Graph Inequalities | Multi-Step With Parenthesis