Stopping Distance (Factors affecting Stopping Distance and calculating it mathematically)
More resources available at www.misterwootube.com
From playlist Formulae and Equations

Absolute Maximum/Minimum (1 of 2: Domain restricted polynomial)
More resources available at www.misterwootube.com
From playlist Applications of Differentiation

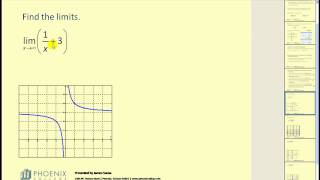
Computing Limits from a Graph with Infinities
In this video I do an example of computing limits from a graph with infinities.
From playlist Limits

KS5 - Stationary & Turning Points
"Maxima and minima and stationary points."
From playlist Differentiation (AS/Beginner)

Maximum and Minimum Values (Closed interval method)
A review of techniques for finding local and absolute extremes, including an application of the closed interval method
From playlist 241Fall13Ex3
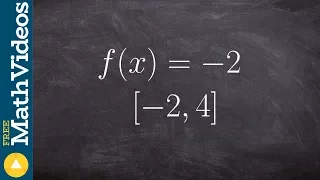
What is the max and min of a horizontal line on a closed interval
👉 Learn how to find the extreme values of a function using the extreme value theorem. The extreme values of a function are the points/intervals where the graph is decreasing, increasing, or has an inflection point. A theorem which guarantees the existence of the maximum and minimum points
From playlist Extreme Value Theorem of Functions

How to end traffic jams once and for all
Have you ever wondered what causes traffic? Indeed, what or who is responsible for the most time-consuming traffic jams? Is it human error? Poor city planning? Accidents? According to experts, the most significant contributor to extreme traffic is poor decision-making by humans. At first
From playlist All About Transportation
AQC 2016 - An Optimal Stopping Approach for Benchmarking Probabilistic Optimizers
A Google TechTalk, June 27, 2016, presented by Walter Vinci (USC) ABSTRACT: We propose a strategy for benchmarking probabilistic optimizers based on an optimal stopping approach. We seek to optimize both the objective function and the number of calls to the solver. A crucial advantage of
From playlist Adiabatic Quantum Computing Conference 2016

Xiaolu Tan: On the martingale optimal transport duality in the Skorokhod space
We study a martingale optimal transport problem in the Skorokhod space of cadlag paths, under finitely or infinitely many marginals constraint. To establish a general duality result, we utilize a Wasserstein type topology on the space of measures on the real value space, and the S-topology
From playlist HIM Lectures 2015

Emilie Kaufmann - Optimal Best Arm Identification with Fixed Confidence
This talk proposes a complete characterization of the complexity of best-arm identification in one-parameter bandit models. We first give a new, tight lower bound on the sample complexity, that is the total number of draws of the arms needed in order to identify the arm with
From playlist Schlumberger workshop - Computational and statistical trade-offs in learning

Pandora's Box with Correlations: Learning and Approximation - Shuchi Chawla
Computer Science/Discrete Mathematics Seminar I Topic: Pandora's Box with Correlations: Learning and Approximation Speaker: Shuchi Chawla Affiliation: University of Wisconsin-Madison Date: April 05, 2021 For more video please visit http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

Fifth SIAM Activity Group on FME Virtual Talk
Title: Deep optimal stopping Speaker: Patrick Cheridito, Professor of Mathematics, ETH Zurich Abstract: I present a deep learning method for optimal stopping problems which directly learns the optimal stopping rule from Monte Carlo samples. As such, it is broadly applicable in situations
From playlist SIAM Activity Group on FME Virtual Talk Series

"Diffusion Approximation and Sequential Experimentation" by Victor Araman
We consider a Bayesian sequential experimentation problem. We identify environments in which the average number of experiments that is conducted per unit of time is large and the informativeness of each individual experiment is low. Under such regimes, we derive a diffusion approximation f
From playlist Thematic Program on Stochastic Modeling: A Focus on Pricing & Revenue Management

Bayesian Optimization in the Wild: Risk-Averse Decisions and Budget Constraints
A Google TechTalk, presented by Anastasia Makarova, 2022/08/23 Google BayesOpt Speaker Series - ABSTRACT: Black-box optimization tasks frequently arise in high-stakes applications such as material discovery or hyperparameter tuning of complex systems. In many of these applications, there i
From playlist Google BayesOpt Speaker Series 2021-2022

Gaoyue Guo - Optimal Skorokhod embedding problem
http://www.lesprobabilitesdedemain.fr/index.html Organisateurs : Céline Abraham, Linxiao Chen, Pascal Maillard, Bastien Mallein et la Fondation Sciences Mathématiques de Paris
From playlist Les probabilités de demain 2016

Fastest Identification in Linear Systems by Alexandre Proutiere
Program Advances in Applied Probability II (ONLINE) ORGANIZERS: Vivek S Borkar (IIT Bombay, India), Sandeep Juneja (TIFR Mumbai, India), Kavita Ramanan (Brown University, Rhode Island), Devavrat Shah (MIT, US) and Piyush Srivastava (TIFR Mumbai, India) DATE: 04 January 2021 to 08 Januar
From playlist Advances in Applied Probability II (Online)

From playlist Contributed talks One World Symposium 2020
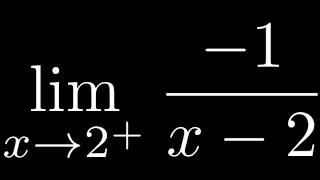
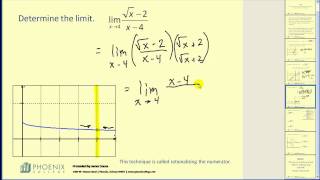
How to Compute a One Sided limit as x approaches from the right
In this video I will show you How to Compute a One Sided limit as x approaches from the right.
From playlist One-sided Limits