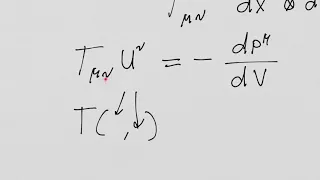Mathematical problems | Calculus of variations | Minimal surfaces
Newton's minimal resistance problem
Newton's minimal resistance problem is a problem of finding a solid of revolution which experiences a minimum resistance when it moves through a homogeneous fluid with constant velocity in the direction of the axis of revolution, named after Isaac Newton, who studied the problem in 1685 and published it in 1687 in his Principia Mathematica. This is the first example of a problem solved in what is now called the calculus of variations, appearing a decade before the brachistochrone problem. Newton published the solution in Principia Mathematica without his derivation and David Gregory was the first person who approached Newton and persuaded him to write an analysis for him. Then the derivation was shared with his students and peers by Gregory. According to I Bernard Cohen, in his Guide to Newton’s Principia, "The key to Newton’s reasoning was found in the 1880s, when the earl of Portsmouth gave his family’s vast collection of Newton’s scientific and mathematical papers to Cambridge University. Among Newton’s manuscripts they found the draft text of a letter, … in which Newton elaborated his mathematical argument. [This]was never fully understood, however, until the publication of the major manuscript documents by D. T. Whiteside [1974], whose analytical and historical commentary has enabled students of Newton not only to follow fully Newton’s path to discovery and proof, but also Newton’s later (1694) recomputation of the surface of least resistance". Even though Newton's model for the fluid was wrong as per our current understanding, the fluid he had considered finds its application in hypersonic flow theory as a limiting case. (Wikipedia).