Pseudorandom number generators
Mersenne Twister
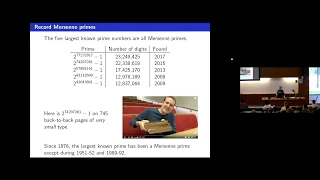
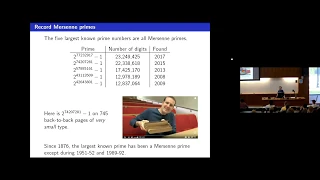
The Mersenne Twister is a general-purpose pseudorandom number generator (PRNG) developed in 1997 by (松本 眞) and (西村 拓士). Its name derives from the fact that its period length is chosen to be a Mersenne prime. The Mersenne Twister was designed specifically to rectify most of the flaws found in older PRNGs. The most commonly used version of the Mersenne Twister algorithm is based on the Mersenne prime . The standard implementation of that, MT19937, uses a 32-bit word length. There is another implementation (with five variants) that uses a 64-bit word length, MT19937-64; it generates a different sequence. (Wikipedia).