History of Maxwell's equations
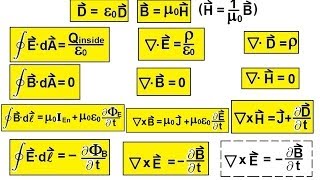
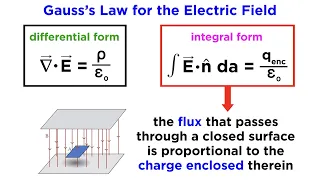
In the beginning of the 19th century, many experimental and theoretical works had been accomplished in the understanding of electromagnetics. In the 1780s, Coulomb's law of electrostatics had been established. In 1825, Ampère published his Ampère's law. Michael Faraday discovered the electromagnetic induction through his experiments and conceptually, he emphasized the lines of forces in this electromagnetic induction. In 1834, Lenz solved the problem of the direction of the induction, and Neumann wrote down the equation to calculate the induced force by change of magnetic flux. However, these experimental results and rules were not well organized and sometimes confusing to scientists. A comprehensive summary of the electrodynamic principles was in urgent need at that time. This work was done by James C. Maxwell through a series of papers published from the 1850s through to the 1870s. In the 1850s, Maxwell was working at the University of Cambridge where he was impressed by Faraday's lines of forces concept. In 1856, he published his 1st paper in electromagnetism: On Faraday's Lines of Force. He tried to use the analogy of incompressible fluid flow to model the magnetic lines of forces. Later, Maxwell moved to King's College London where he actually came into regular contact with Faraday, and became life-long friends. From 1861-1862, Maxwell published a series of 4 papers under the title of On Physical Lines of Force. In these papers, he used mechanical models, such as rotating vortex tubes, to model the electromagnetic field. He also modeled the vacuum as a kind of insulating elastic medium to account for the stress of the magnetic lines of force given by Faraday. These works had already laid the basis of the formulation of the Maxwell's equations. Moreover, the 1862 paper already derived the speed of light c from the expression of the velocity of the electromagnetic wave in relation to the vacuum constants. The final form of Maxwell's equations was published in 1865 A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field, in which the theory is formulated in strictly mathematical form. In 1873, Maxwell published A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism as a summary of his work on electromagnetism. In summary, Maxwell's equations successfully unified theories of light and electromagnetism, which is one of the great unifications in physics. Later, Oliver Heaviside studied Maxwell's A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism and employed vector calculus to synthesize Maxwell's over 20 equations into the 4 recognizable ones which modern physicists use. Maxwell's equations also inspired Albert Einstein in developing the theory of special relativity. The experimental proof of Maxwell's equations was demonstrated by Heinrich Hertz in a series of experiments in the 1890s. After that, Maxwell's equations were fully accepted by scientists. (Wikipedia).