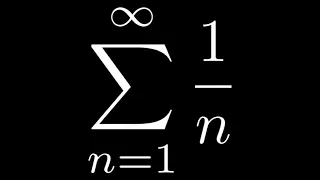Harmonic series (mathematics)
In mathematics, the harmonic series is the infinite series formed by summing all positive unit fractions: The first terms of the series sum to approximately , where is the natural logarithm and is the Euler–Mascheroni constant. Because the logarithm has arbitrarily large values, the harmonic series does not have a finite limit: it is a divergent series. Its divergence was proven in the 14th century by Nicole Oresme using a precursor to the Cauchy condensation test for the convergence of infinite series. It can also be proven to diverge by comparing the sum to an integral, according to the integral test for convergence. Applications of the harmonic series and its partial sums include Euler's proof that there are infinitely many prime numbers, the analysis of the coupon collector's problem on how many random trials are needed to provide a complete range of responses, the connected components of random graphs, the block-stacking problem on how far over the edge of a table a stack of blocks can be cantilevered, and the average case analysis of the quicksort algorithm. (Wikipedia).