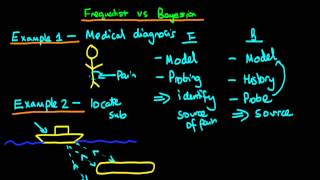
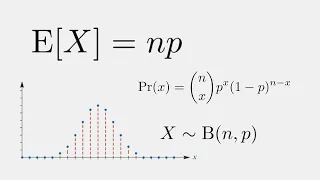Frequentist probability
Frequentist probability or frequentism is an interpretation of probability; it defines an event's probability as the limit of its relative frequency in many trials (the long-run probability). Probabilities can be found (in principle) by a repeatable objective process (and are thus ideally devoid of opinion). The continued use of frequentist methods in scientific inference, however, has been called into question. The development of the frequentist account was motivated by the problems and paradoxes of the previously dominant viewpoint, the classical interpretation. In the classical interpretation, probability was defined in terms of the principle of indifference, based on the natural symmetry of a problem, so, e.g. the probabilities of dice games arise from the natural symmetric 6-sidedness of the cube. This classical interpretation stumbled at any statistical problem that has no natural symmetry for reasoning. (Wikipedia).