
Fixed Effects and Random Effects
Brief overview in plain English of the differences between the types of effects. Problems with each model and how to overcome them.
From playlist Experimental Design

Review of Linear Time Invariant Systems
http://AllSignalProcessing.com for more great signal-processing content: ad-free videos, concept/screenshot files, quizzes, MATLAB and data files. Review: systems, linear systems, time invariant systems, impulse response and convolution, linear constant-coefficient difference equations
From playlist Introduction and Background

position:fixed juddering (real device)
Mirroring my phone to computer to record, you can see the same position:fixed juddering occurs in iOS 5.1.1
From playlist position:fixed
position:fixed juddering (simulator)
Example of position:fixed on iOS 5 juddering
From playlist position:fixed

Fuzzy control of inverted pendulum
Fuzzy control of inverted pendulum, State-feedback controller is designed based on T-S fuzzy model with the consideration of system stability and performance.
From playlist Demonstrations
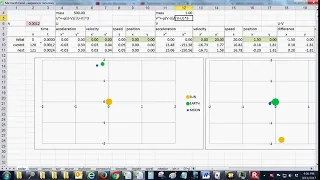
A solar system, a simulation made with Excel
An Excel simulation of the solar system. You can see how things are recursively computed: the mutual gravity force from the locations, the accelerations, the velocities, and finally the updated locations. The solar eclipse is also shown. This is clip is intended to illustrate Chapter 24 Ap
From playlist Physics simulations
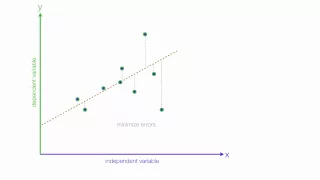
An Introduction to Linear Regression Analysis
Tutorial introducing the idea of linear regression analysis and the least square method. Typically used in a statistics class. Playlist on Linear Regression http://www.youtube.com/course?list=ECF596A4043DBEAE9C Like us on: http://www.facebook.com/PartyMoreStudyLess Created by David Lon
From playlist Linear Regression.

The Ferris Wheel - Trigonometric Function Model (1 of 3: Setting up the equation)
More resources available at www.misterwootube.com
From playlist Trigonometric Functions and Graphs

Statistical Rethinking 2023 - 12 - Multilevel Models
Course details: https://github.com/rmcelreath/stat_rethinking_2023 Intro music: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E0yoH1LnQFI Outline 00:00 Introduction 04:29 Multilevel models 13:50 Partial pooling 16:53 Reedfrogs 22:17 Hyperparameter tuning through crossvalidation 31:23 Pause 32:02 Learn
From playlist Statistical Rethinking 2023

D E Logan - Two-channel Kondo physics in impurity chains and rings
PROGRAM: The ICTS Condensed Matter Programme 2011 Venue: Indian Insitute of Science, Bangalore Date: Friday 09 Dec, 2011 - Thursday 22 Dec, 2011 DESCRIPTION: The ICTS Condensed Matter Programme 2011 (ICMP 2011) consists of a 10 day Winter School (December 9 to December 18) followed by a 4
From playlist The ICTS Condensed Matter Programme 2011

Statistical Rethinking Winter 2019 Lecture 15
Lecture 15 of the Dec 2018 through March 2019 edition of Statistical Rethinking: A Bayesian Course with R and Stan. Covers Chapter 13, Multilevel Models.
From playlist Statistical Rethinking Winter 2019

Daniel Friedan - Where does quantum field theory come from?
Daniel Friedan (Rutgers Univ.) Where does quantum field theory come from? This will be an interim report on a long-running project to construct a mechanism that produces spacetime quantum field theory; to indentify possible exotic, non-canonical low- energy phenomena in SU(2) and SU(3) gau
From playlist Conférence à la mémoire de Vadim Knizhnik

Slava Rychkov - Random Field Ising Model and Parisi-Sourlas Supersymmetry (4/4)
Numerical evidence suggests that the Random Field Ising Model loses Parisi-Sourlas SUSY and the dimensional reduction property somewhere between 4 and 5 dimensions, while a related model of branched polymers retains these features in any d. I will present a recent theory, developed in 2019
From playlist Slava Rychkov - Random Field Ising Model and Parisi-Sourlas Supersymmetry

ICTS Special Colloquium by Bruce Walsh
Second Bangalore School on Population Genetics and Evolution URL: http://www.icts.res.in/program/popgen2016 DESCRIPTION: Just as evolution is central to our understanding of biology, population genetics theory provides the basic framework to comprehend evolutionary processes. Population
From playlist Second Bangalore School on Population Genetics and Evolution
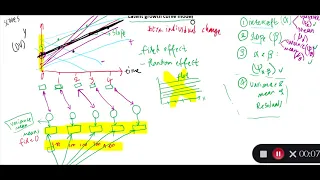
Latent Growth Curve Modeling | Part 2 | Structural Equation Modeling
In the second installment of this video series, I will discuss the essential concepts in Growth Curve Modeling within the Structural Equation Modeling framework.
From playlist Growth Curve Models

Inspired by https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EYkBctqyKic
From playlist Handmade geometric toys

Statistical Rethinking 2022 Lecture 13 - Multi-Multilevel Models
Slides and other course materials: https://github.com/rmcelreath/stat_rethinking_2022 Music: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R2d2spnXyLA Glass blowing: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=apDH4YEv3_c Chapters: 00:00 Introduction 08:25 Multiple cluster types 29:00 Multilevel predictions 38:39
From playlist Statistical Rethinking 2022

