
http://www.teachastronomy.com/ There is no science without evidence. When a scientist makes an assertion he must back it up with evidence. The evidence could be evidence that is physical evidence. It could be evidence gathered from telescopes, or microscopes, or other mechanisms we have
From playlist 01. Fundamentals of Science and Astronomy

Teach Astronomy - Testing a Hypothesis
http://www.teachastronomy.com/ One of the basic tasks of science is to test hypotheses. A hypothesis is a description of a set of data, a model, usually a mathematical description in most branches of science. To test a hypothesis we need data of sufficient quantity and quality, and our a
From playlist 01. Fundamentals of Science and Astronomy
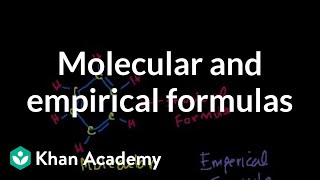
Molecular and Empirical Formulas
Introduction to molecular and empirical formulas. Calculating molecular mass. More free lessons at: http://www.khanacademy.org/video?v=gfBcM3uvWfs
From playlist Chemistry

Teach Astronomy - The Evidence of Astronomy
http://www.teachastronomy.com/ There's very little direct evidence in astronomy. In a few cases we've been lucky enough to have meteorites falling from space. We've even had a few free samples of Mars. But most of the evidence of astronomy is gathered remotely. We've sent spacecrafts t
From playlist 01. Fundamentals of Science and Astronomy

What is the difference between theoretical and experimental physics?
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel for all the latest from World Science U. Visit our Website: http://www.worldscienceu.com/ Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/worldscienceu Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/worldscienceu
From playlist Science Unplugged: Physics

Statistics: Ch 9 Hypothesis Testing (1 of 34) What is a Hypothesis?
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! To donate: http://www.ilectureonline.com/donate https://www.patreon.com/user?u=3236071 We will learn a hypothesis is: a) A supposition or a proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point f
From playlist STATISTICS CH 9 HYPOTHESIS TESTING

http://www.teachastronomy.com/ Science is and must be objective. It must be based on observational data and experimentation. The results must be published so that other people can check or confirm or independently measure the same things. Science depends on this, but there is a social e
From playlist 01. Fundamentals of Science and Astronomy
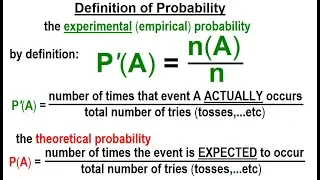
Statistics: Ch 4 Probability in Statistics (20 of 74) Definition of Probability
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! To donate: http://www.ilectureonline.com/donate https://www.patreon.com/user?u=3236071 We will learn the “strict” definition of experimental (empirical) and theoretical probability. Next video in this series can be seen
From playlist STATISTICS CH 4 STATISTICS IN PROBABILITY

What is a hypothesis test? The meaning of the null and alternate hypothesis, with examples. Overview of test statistics and confidence levels.
From playlist Hypothesis Tests and Critical Values

CGSR | How Nations Actually Succeed in Rivalries: The Societal Sources of Competitive Advantage
How Nations Actually Succeed in Rivalries: The Societal Sources of Competitive Advantage by Mike Mazarr Abstract: Nations rise and fall, succeed or fail in rivalries, and enjoy stability or descend into chaos because of a complex web of factors. One critical component of any such recipe i
From playlist Center for Global Security Research

Mayans and Teotihuacan | World History | Khan Academy
An overview of the Mayan civilization as well as the great city of Teotihuacan. Watch the next lesson: https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/world-history/ancient-medieval/civilizations-in-the-americas/v/chavin-nazca-moche-huari-and-tiwanaku-civilizations World History on Khan Academy:
From playlist 600 BCE - 600 CE Second-Wave Civilizations | AP World History | Khan Academy

Sasanian Iran: A Personal View - Michael R. Jackson Bonner
The Author’s Voice Topic: Sasanian Iran: A Personal View Speaker: Michael R. Jackson Bonner Affiliation: Canadian writer, political adviser and independent historian of Iran September 16, 2021 I will discuss how I came to write The Last Empire of Iran and why. My main motivation was to
From playlist Historical Studies

Soissons and the End of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman empire was not a single event, but a cultural and economic shift that took centuries. The empire's last stand may have been a kingdom in central France. It is history that deserves to be remembered. This is original content based on research by The History Gu
From playlist Europe

Mark Balaguer - What Are the Things of Existence?
How many different kinds of 'things' are there? What are the fewest number of things that can characterize existence and do so exhaustively? In other words, what are the most basic building blocks of everything we see and know? From what things can all that exists be constructed? Are thing
From playlist Exploring Metaphysics - Closer To Truth - Core Topic

What Research Teaches About Making Languages Easy to Learn
What Research Teaches About Making Languages Easy to Learn: Andreas Stefik's team runs experiments to evaluate ease of programming and has developed its own language named Quorum.
From playlist Programming Podcast

Physics Professor watches "the goop lab" - Sixty Symbols
Professor Philip Moriarty watched episode 5 of the goop lab, which focuses on energy. More links and info below ↓ ↓ ↓ the goop lab on Netflix: https://www.netflix.com/title/80244690 More videos with Phil: http://bit.ly/Prof_Moriarty Phil is a physics professor at The University of Not
From playlist Professor Moriarty - Sixty Symbols

How to Talk to a Science Denier - with Lee McIntyre
Many people reject scientific expertise and prefer ideology to facts. Lee McIntyre argues that anyone can and should fight back against science deniers. Watch the Q&A: https://youtu.be/2jTiXCLzMv4 Lee's book "How to Talk to a Science Denier" is out now: https://geni.us/leemcintyre “Climat
From playlist Livestreams

How Irrationality Created Modern Science - with Michael Strevens
Michael Strevens argues that science came about only once thinkers stumbled upon the idea that scientific breakthroughs could be accomplished by breaking the rules of logical argument. Get Michael's book: https://geni.us/knolmach Watch the Q&A: https://youtu.be/ZOq--OyMQEo Modern science
From playlist Livestreams

Teach Astronomy - Pseudoscience
http://www.teachastronomy.com/ A pseudoscience is something that pretends to be scientific but is not. Science follows a rigorous method which relies on the sharing of data, the basis in observations, and the fact that any scientist can assert something, but it has to be supported by evid
From playlist 01. Fundamentals of Science and Astronomy

Review: Inglorious Empire by Shashi Tharoor
Inglorious Empire on Amazon: https://www.amazon.com/shop/caspianreport Speech by Shashi Tharoor OxfordUnion: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f7CW7S0zxv4 Support CaspianReport on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/CaspianReport PayPal: https://www.paypal.me/CaspianReport Bitcoin: 1MwRNXWW
From playlist The Bookshelf