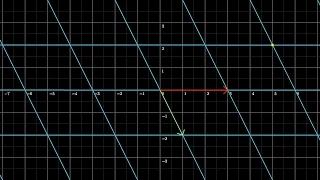
Introduction to Linear Functions and Slope (L10.1)
This lesson introduces linear functions, describes the behavior of linear function, and explains how to determine the slope of a line given two points. Video content created by Jenifer Bohart, William Meacham, Judy Sutor, and Donna Guhse from SCC (CC-BY 4.0)
From playlist Introduction to Functions: Function Basics

Weil-Petersson currents by Georg Schumacher
DISCUSSION MEETING ANALYTIC AND ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY DATE:19 March 2018 to 24 March 2018 VENUE:Madhava Lecture Hall, ICTS, Bangalore. Complex analytic geometry is a very broad area of mathematics straddling differential geometry, algebraic geometry and analysis. Much of the interactions be
From playlist Analytic and Algebraic Geometry-2018

STOP Doing Deadlifts Like This (SAVE YOUR SPINE!) ft. Dr. Stuart McGill
If you’ve ever hurt your back deadlifting or are afraid to do deadlifts in fear that you will end up hurting yourself, you’re not alone. There are 5 reasons why injuries are common on the deadlift. I’ll share with you what these reasons are, how to determine the right deadlift form for you
From playlist EXERCISE FORM TIPS

Brent Pym: Holomorphic Poisson structures - lecture 1
CIRM VIRTUAL EVENT Recorded during the research school "Geometry and Dynamics of Foliations " the April 28, 2020 by the Centre International de Rencontres Mathématiques (Marseille, France) Filmmaker: Guillaume Hennenfent Find this video and other talks given by worldwide mathematicians on
From playlist Virtual Conference

HOW IT WORKS: Old Typesetting Machines
Describes the operation of automatic type equipment.
From playlist HOW IT WORKS

Solving two step equations with a rational expression on one side
👉 Learn how to solve two step rational linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. A rational equation is an equation containing at least one fraction whose numerator and (or) denominator are polynomials. To solve for a variable in a
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations with a Rational Fraction
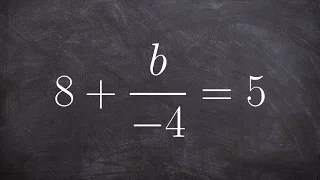
Solving a two step equation including subtraction and multiplication
👉 Learn how to solve two step linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. To solve for a variable in a two step linear equation, we first isolate the variable by using inverse operations (addition or subtraction) to move like terms to
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations with a Fraction
DAT_012 - Phonemic Transcription - VLC Series #2
In this short combinatory video (screencast and e-lecture), first recorded in 2013 and updated in 2022, Prof. Handke discusses the phonemic transcription of one of the VLC-Transcription Exercises (here VLC Transcription Series #2) and points out problematic aspects as well as aspects of co
From playlist Data Analysis - Phonemic Transcription, the VLC Series
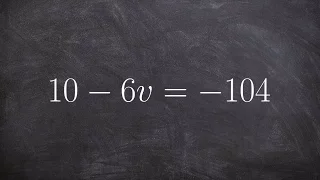
Solving for X in an equation using subtraction and division
👉 Learn how to solve two step linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. To solve for a variable in a two step linear equation, we first isolate the variable by using inverse operations (addition or subtraction) to move like terms to
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations

Secondary products in SUSY QFT by Tudor Dimofte
Program: Quantum Fields, Geometry and Representation Theory ORGANIZERS : Aswin Balasubramanian, Saurav Bhaumik, Indranil Biswas, Abhijit Gadde, Rajesh Gopakumar and Mahan Mj DATE & TIME : 16 July 2018 to 27 July 2018 VENUE : Madhava Lecture Hall, ICTS, Bangalore The power of symmetries
From playlist Quantum Fields, Geometry and Representation Theory
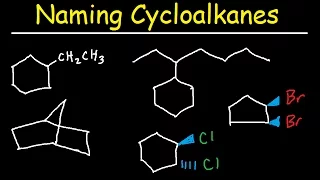
Naming Cycloalkanes With Substituents, Cis & Trans, Bicyclo Alkane Nomenclature
This organic chemistry video tutorial explains how to name cycloalkanes with substituents and with cis and trans isomers. It covers examples such as cyclopropane, cyclobutane, cyclopentane, cyclohexane, cycloheptane, and cyclooctane, This video also discusses the nomenclature of bicyclic
From playlist New Organic Chemistry Playlist

Classical Gravitational Scattering (Lecture 3) by Shiraz Minwalla
PROGRAM KAVLI ASIAN WINTER SCHOOL (KAWS) ON STRINGS, PARTICLES AND COSMOLOGY (ONLINE) ORGANIZERS Francesco Benini (SISSA, Italy), Bartek Czech (Tsinghua University, China), Dongmin Gang (Seoul National University, South Korea), Sungjay Lee (Korea Institute for Advanced Study, South Korea
From playlist Kavli Asian Winter School (KAWS) on Strings, Particles and Cosmology (ONLINE) - 2022

👉 Learn how to solve two step linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. To solve for a variable in a two step linear equation, we first isolate the variable by using inverse operations (addition or subtraction) to move like terms to
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations

👉 Learn how to solve two step linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. To solve for a variable in a two step linear equation, we first isolate the variable by using inverse operations (addition or subtraction) to move like terms to
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations
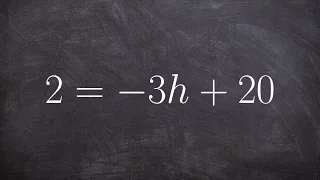
👉 Learn how to solve two step linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. To solve for a variable in a two step linear equation, we first isolate the variable by using inverse operations (addition or subtraction) to move like terms to
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations

Geometric Algebra in 3D - The Vector-Bivector Product (Part 1)
After having set up G(3), let's now investigate a particular geometric product, namely, the product between vector and bivector. We'll see that such a product in general splits into a vector part and the trivector part. Similar to the geometric product between vectors, we'll call the lower
From playlist Math
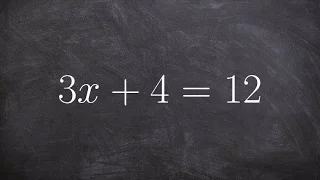
👉 Learn how to solve two step linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. To solve for a variable in a two step linear equation, we first isolate the variable by using inverse operations (addition or subtraction) to move like terms to
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations

👉 Learn how to solve two step linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. To solve for a variable in a two step linear equation, we first isolate the variable by using inverse operations (addition or subtraction) to move like terms to
From playlist Solve Two Step Equations