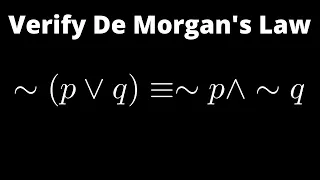Articles containing proofs | Rules of inference | Duality theories | Boolean algebra | Theorems in propositional logic
De Morgan's laws
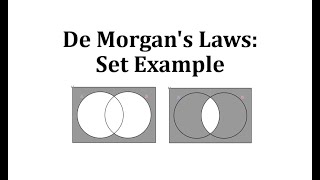
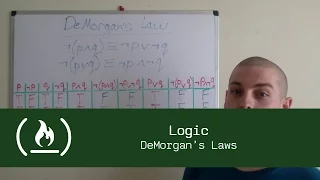
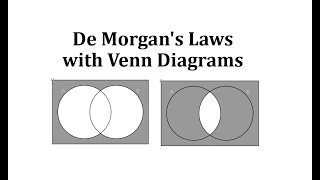
In propositional logic and Boolean algebra, De Morgan's laws, also known as De Morgan's theorem, are a pair of transformation rules that are both valid rules of inference. They are named after Augustus De Morgan, a 19th-century British mathematician. The rules allow the expression of conjunctions and disjunctions purely in terms of each other via negation. The rules can be expressed in English as: * The negation of a disjunction is the conjunction of the negations * The negation of a conjunction is the disjunction of the negations or * The complement of the union of two sets is the same as the intersection of their complements * The complement of the intersection of two sets is the same as the union of their complements or * not (A or B) = (not A) and (not B) * not (A and B) = (not A) or (not B) where "A or B" is an "inclusive or" meaning at least one of A or B rather than an "exclusive or" that means exactly one of A or B. In set theory and Boolean algebra, these are written formally as where * and are sets, * is the complement of , * is the intersection, and * is the union. In formal language, the rules are written as and where * P and Q are propositions, * is the negation logic operator (NOT), * is the conjunction logic operator (AND), * is the disjunction logic operator (OR), * is a metalogical symbol meaning "can be replaced in a logical proof with". Applications of the rules include simplification of logical expressions in computer programs and digital circuit designs. De Morgan's laws are an example of a more general concept of mathematical duality. (Wikipedia).