
Learning how to graph and determine characteristics of a quadratic using vertex formula
👉 Learn how to graph quadratics in standard form. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetry, to p
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | ax^2+bx+c

AMMI 2022 Course "Geometric Deep Learning" - Lecture 11 (Beyond Groups) - Petar Veličković
Video recording of the course "Geometric Deep Learning" taught in the African Master in Machine Intelligence in July 2022 by Michael Bronstein (Oxford), Joan Bruna (NYU), Taco Cohen (Qualcomm), and Petar Veličković (DeepMind) Lecture 11: Category Theory • Set category • Functors • Natural
From playlist AMMI Geometric Deep Learning Course - Second Edition (2022)

Lecture 7: From Equivariance to Naturality - Pim de Haan
Video recording of the First Italian School on Geometric Deep Learning held in Pescara in July 2022. Slides: https://www.sci.unich.it/geodeep2022/slides/2022-07-27%20Naturality%20@%20First%20Italian%20GDL%20Summer%20School.pdf
From playlist First Italian School on Geometric Deep Learning - Pescara 2022

Learn how to graph the parent graph of a quadratic equation in standard form using a table
👉 Learn the basics to understanding graphing quadratics. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetr
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | Essentials

Graphing a quadratic using a table
👉 Learn how to graph quadratics in standard form. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetry, to p
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | x^2+bx+c
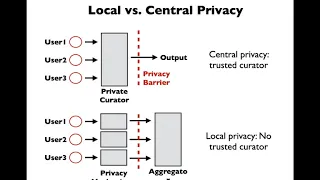
Profile-based Privacy for Locally Private Computations
A Google TechTalk, 2020/7/30, presented by Kamalika Chaudhuri, UCSD ABSTRACT: Differential privacy has emerged as a gold standard in privacy-preserving data analysis. A popular variant commonly used for federated learning is local differential privacy, where the data holder is the trusted
From playlist 2020 Google Workshop on Federated Learning and Analytics
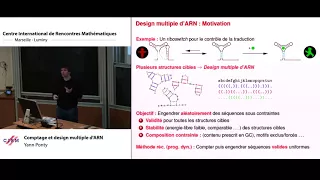
Yann Ponty : Comptage et design multiple d'ARN
Abstract: Les Acides RiboNucléiques (ARN) sont des biopolymères linéaires omniprésents dans notre organisme, pouvant être codés comme des séquences sur un alphabet A,C,G,U. Ces molécules se replient sur elles-mêmes, établissant des liaisons hydrogènes d'où découlent l'appariement de certai
From playlist Probability and Statistics

How to graph the inverse sine given the graph of sine
👉 Learn how to evaluate an expression with the composition of a function and a function inverse. Just like every other mathematical operation, when given a composition of a trigonometric function and an inverse trigonometric function, you first evaluate the one inside the parenthesis. We
From playlist Evaluate a Composition of Inverse Trigonometric Functions

Math tutorial for evaluating the composition of the sine and tangent function
👉 Learn how to evaluate an expression with the composition of a function and a function inverse. Just like every other mathematical operation, when given a composition of a trigonometric function and an inverse trigonometric function, you first evaluate the one inside the parenthesis. We
From playlist Evaluate a Composition of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Graphing a quadratic by using a table and the axis of symmetry
👉 Learn how to graph quadratics in standard form. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetry, to p
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | x^2+bx+c

The amazing power of composition - Toniann Pitassi
https://www.math.ias.edu/avi60/agenda More videos on http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

How to determine the domain and range of a quadratic using its vertex
👉 Learn the basics to understanding graphing quadratics. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetr
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | Essentials

What do I have to know to graph a quadratic in standard form
👉 Learn the basics to understanding graphing quadratics. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetr
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | Essentials

Team 2854 High Tech HS presentation 2014
In Moody's Mega Math Challenge 2014, more than 5,000 high school students across the U.S. set out to determine what makes a school lunch easy on the stomach...and the wallet. Participants pored over data, crunched numbers, and used mathematical analysis to determine how school lunches can
From playlist M3 Challenge 2014 Team Presentations
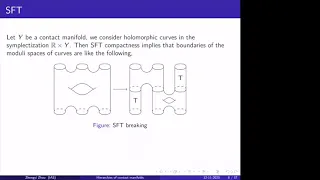
Hierarchies of contact manifolds via rational SFT - Zhengyi Zhou
IAS/PU-Montreal-Paris-Tel-Aviv Symplectic Geometry Topic: Hierarchies of contact manifolds via rational SFT Speaker: Zhengyi Zhou Affiliation: Member, School of Mathematics Date: December 11, 2020 For more video please visit http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

How to graph a quadratic equation in standard form
👉 Learn the basics to understanding graphing quadratics. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetr
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | Essentials
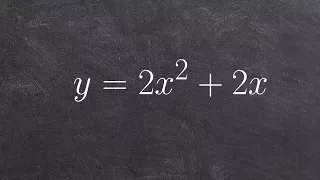
Graphing a quadratic function in standard form
👉 Learn how to graph quadratics in standard form. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetry, to p
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | ax^2+bx

Graphing a quadratic function in standard form
👉 Learn how to graph quadratics in standard form. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetry, to p
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | ax^2+bx

Scheduling for AUTOSAR Architecture Models in Simulink
This video covers timing constraints for Architecture models using AUTOSAR Blockset. We show how you can configure the execution order using Schedule Editor, illustrate its impact, and export a timing model. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
From playlist Modeling and Simulation | Developer Tech Showcase

Graphing a quadratic equation using a table of values
👉 Learn how to graph quadratics in standard form. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest exponent in the variable(s) is 2. To graph a quadratic equation, we make use of a table of values and the fact that the graph of a quadratic is a parabola which has an axis of symmetry, to p
From playlist Graph a Quadratic in Standard Form | x^2+bx+c