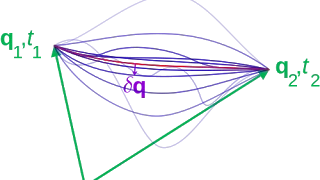
The Beltrami Identity is a necessary condition for the Euler-Lagrange equation (so if it solves the E-L equation, it solves the Beltrami identity). Here it is derived from the total derivative of the integrand (e.g. Lagrangian).
From playlist Physics

I define one of the most important constants in mathematics, the Euler-Mascheroni constant. It intuitively measures how far off the harmonic series 1 + 1/2 + ... + 1/n is from ln(n). In this video, I show that the constant must exist. It is an open problem to figure out if the constant is
From playlist Series

If macro laws and micro laws conflict, does that mean our understanding of physics is wrong?
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel for all the latest from World Science U. Visit our Website: http://www.worldscienceu.com/ Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/worldscienceu Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/worldscienceu
From playlist Science Unplugged: Physics

The golden ratio | Lecture 3 | Fibonacci Numbers and the Golden Ratio
The classical definition of the golden ratio. Two positive numbers are said to be in the golden ratio if the ratio between the larger number and the smaller number is the same as the ratio between their sum and the larger number. Phi=(1+sqrt(5))/2 approx 1.618. Join me on Coursera: http
From playlist Fibonacci Numbers and the Golden Ratio

A problem with Bohmian Mechanics? Contextuality
'Contextuality' might mean that there are no alternatives to Quantum mechanics that are sensible. Given Quantum isn't sensible either, there may just not be any sensible theories at all. RUSSIAN SUBS AVAILABLE. Thank you to my amazing friend Daniel who offered his time to do this!
From playlist Old Quantum Mechanics Videos

Oily-Maccaroni: A Curious Limit Definition!
Help me create more free content! =) https://www.patreon.com/mathable Merch :v - https://teespring.com/stores/papaflammy https://www.amazon.com/shop/flammablemaths https://shop.spreadshirt.de/papaflammy Become a Member of the Flammily! :0 https:
From playlist Number Theory
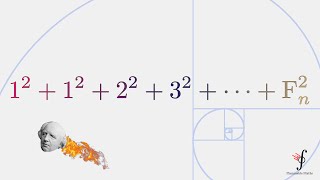
A Beautiful Visual Interpretation - The Sum of Squares of the Fibonacci Numbers.
Help me create more free content! =) https://www.patreon.com/mathable Merch :v - https://papaflammy.myteespring.co/ https://www.amazon.com/shop/flammablemaths https://shop.spreadshirt.de/papaflammy Become a Member of the Flammily! :0 https://www.youtub
From playlist Number Theory

Here I go over an example of using the variational principle to find an upper bound on the ground state energy of a neat potential - the infinite triangular well. Hope you found this video helpful, please post in the comments below anything I can do to improve future videos, or suggestion
From playlist Quantum Mechanics
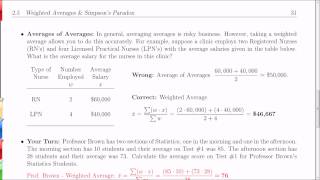
Chapter 2.5 Weighted Averages and Simpson's Paradox
Chapter 2.5 from "Introduction to Statistics, Think & Do" by Scott Stevens (http://www.StevensStats.com) Textbook from Publisher, $29.95 print, $9.95 PDF http://www.centerofmathematics.com/wwcomstore/index.php/thinkdov4-1.html Textbook from Amazon: https://amzn.to/2zJRCjL
From playlist Statistics Lecture Videos

Math for Liberal Studies - Lecture 2.7.2 Hamilton's Method and Apportionment Paradoxes
This is the second video lecture for Math for Liberal Studies Section 2.7: Apportionment. In this video, we learn how to use Hamilton's Method to assign a whole number of seats to each state based on their population. We also discuss several "paradoxes" that result from this method.
From playlist Math for Liberal Studies Lectures

2. Utilities, Endowments, and Equilibrium
Financial Theory (ECON 251) This lecture explains what an economic model is, and why it allows for counterfactual reasoning and often yields paradoxical conclusions. Typically, equilibrium is defined as the solution to a system of simultaneous equations. The most important economic mode
From playlist Financial Theory with John Geanakoplos

Chapter 1.3: Lying with Statistics and Percentages
Chapter 1.3 from "Introduction to Statistics, Think & Do" by Scott Stevens (http://www.StevensStats.com) Textbook from Publisher, $29.95 print, $9.95 PDF http://www.centerofmathematics.com/wwcomstore/index.php/thinkdov4-1.html Textbook from Amazon: https://amzn.to/2zJRCjL
From playlist Statistics Lecture Videos

Relativity 11e - spherical bodies and black holes V
Relativity playlist: http://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLF56602BAC693237E
From playlist Relativity

Terry Karl, Gildred Professor of Latin American Studies and professor of Political Science at Stanford University, discusses overcoming the resource curse. The Energy Seminar meets weekly during the academic year. For a list of upcoming talks, visit the events page at the Woods Institute f
From playlist Lecture Collection | Energy Seminar

15 minute presentation:archiving large-scale digitized collections of historic magazines
From playlist New Directions for Digital Scholarship

A nice Fibonacci reciprocal sum!
We calculate a nice sum involving reciprocals of 1+f_{2n+1}, where f_m is the mth Fibonacci number. http://www.michael-penn.net http://www.randolphcollege.edu/mathematics/
From playlist Identities involving Fibonacci numbers

PBS Member Stations rely on viewers like you. To support your local station, go to: http://to.pbs.org/DonateOKAY ↓ More info and sources below ↓ You guys asked me questions, so I answered them! SUBSCRIBE and get more great science, it's FREE! -- http://bit.ly/iotbs_sub Engineering RuBi
From playlist Be Smart - LATEST EPISODES!
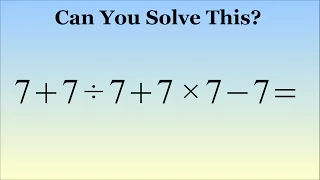
What Is 7 + 7 ÷ 7 + 7 × 7 - 7 = ? The Correct Answer Explained
What is 7 + 7÷7 + 7×7 - 7 = ? This problem has been shared on Facebook and Twitter millions of times and confused many people. In this video, I present two different methods of solving for the correct answer. My blog post for this video http://wp.me/p6aMk-4EX Videos about the order of op
From playlist Viral Math Memes

How to Determine if Functions are Linearly Independent or Dependent using the Definition
How to Determine if Functions are Linearly Independent or Dependent using the Definition If you enjoyed this video please consider liking, sharing, and subscribing. You can also help support my channel by becoming a member https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCr7lmzIk63PZnBw3bezl-Mg/join Th
From playlist Zill DE 4.1 Preliminary Theory - Linear Equations

Dr. Lew explains important cultural trends with self-referential symmetric rhyme. Enjoy word sequences you may not have thought of, and won't hear anywhere else.
From playlist G4G12 Videos