
An A chord is made from combining the notes A, C# and E
From playlist Music Lessons

What is a line segment and ray
👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

RailsConf 2022 - Testing legacy code when you dislike tests (and legacy code) by Maeve Revels
Are you supporting legacy code? Would you like to stop? A good testing strategy can transform legacy code into living code that is resilient and easy to evolve. Learn why legacy code is so difficult to maintain and identify where tests can make the most impact. Not just any tests, though!
From playlist RailsConf 2022

What is the definition of a ray
👉 Learn essential definitions of points, lines, and planes. A point defines a position in space. A line is a set of points. A line can be created by a minimum of two points. A plane is a flat surface made up of at least three points. A plane contains infinite number of lines. A ray is a li
From playlist Points Lines and Planes

MIT 6.849 Geometric Folding Algorithms: Linkages, Origami, Polyhedra, Fall 2012 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/6-849F12 Instructor: Erik Demaine This class introduces the pita form and Alexandrov-Pogorelov Theorem. D-forms are discussed with a construction exercise, followed
From playlist MIT 6.849 Geometric Folding Algorithms, Fall 2012

RubyConf 2019 - Bursting at the Seams by David McDonald
Bursting at the Seams by David McDonald Our industry remains in its infancy but we've had many important contributions to how we all think and talk about design. In order to tighten the existing gap between where theory and practice meet, we need to continue to add to our shared vocabula
From playlist RubyConf 2019

Blender Tutorial | How To Create Modular Game Assets In Blender | Session 08 | #blender | #gamedev
Don’t forget to subscribe! In this Blender tutorial, you will learn to create Modular game assets in Blender. In this tutorial series, we will be covering how to create game-ready assets using modularity. Modularity is about creating bigger environments with smaller, interchangeable piec
From playlist Create Modular Game Assets In Blender

Pennsylvania's 50-Year-Old Coal Fire
SciShow takes you to Centralia, Pennsylvania, site of one of the oldest, biggest coal fires in the United States, and explains the chemistry of spontaneous combustion. ---------- Like SciShow? Want to help support us, and also get things to put on your walls, cover your torso and hold your
From playlist Uploads

Class 2: Univeresality & Simple Folds
MIT 6.849 Geometric Folding Algorithms: Linkages, Origami, Polyhedra, Fall 2012 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/6-849F12 Instructor: Erik Demaine This class begins with a folding exercise of numerical digits. Questions discussed cover strip folding in the context of efficienc
From playlist MIT 6.849 Geometric Folding Algorithms, Fall 2012

Elementary Introduction To Wolfram Language - Machine Learning | Session 29 | #datascience
Don’t forget to subscribe! This project series is an elementary introduction to the wolfram language. Developed by Wolfram Research, it is a multi-paradigm programming language. It is the language of the mathematical symbolic computation program Mathematica. It is scalable for programs
From playlist Elementary Introduction To Wolfram Language
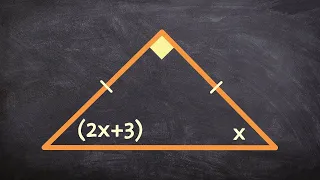
Using the Isosceles triangle theorem to find the measure of x
👉 Learn how to find the missing side of a triangle. A triangle is a polygon with three sides. Triangles are classified on the basis of the angles or on the basis of the sides. The classification of a triangle on the basis of the sides are: scalene, isosceles, and equilateral triangles. A
From playlist Triangles

DevOpsDays Boston 2019 - Infrastructure As Data by Tobias Macey
Infrastructure As Data by Tobias Macey Our ability to build and maintain infrastructure has been made easier and faster by the introduction of technologies such as server virtualization, cloud platforms, container orchestrators, and configuration management frameworks. This has led to the
From playlist DevOpsDays Boston 2019

The M1 helmet, an icon of World War II - here's a handy guide. VISIT www.markfelton.co.uk for more great content!
From playlist Helmets
RubyConf 2016 - Surgically Refactoring Ruby with Suture by Justin Searls
RubyConf 2016 - Surgically Refactoring Ruby with Suture by Justin Searls The next feature means changing legacy code. The estimate just says "PAIN" in red ink. Your hands tremble as you claim the card from the wall. For all of Ruby's breakthroughs, refactoring is as painful as 2004, when
From playlist RubyConf 2016

What is the Pythagorean Inequality Theorem
👉 Learn all about classifying triangles. A triangle is a closed figure with three sides. A triangle can be classified based on the length of the sides or based on the measure of the angles. To classify a triangle based on the length of the sides, we have: equilateral (3 sides are equal), i
From playlist Triangles