
From playlist Physics - Newton's law videos for analysis

From playlist Physics - Newton's law videos for analysis

From playlist Physics - Newton's law videos for analysis

What is a Newton? An Explanation
This video goes over an explanation of the metric unit for force which is the newton. The newton is the derived unit in the metric system for force. A force is a push or a pull. One newton is equal to the force that would give a one kilogram mass an acceleration of one meter per second s
From playlist Mechanics

From playlist Physics - Newton's law videos for analysis

From playlist Physics - Newton's law videos for analysis

From playlist Physics - Newton's law videos for analysis

From playlist Physics - Newton's law videos for analysis
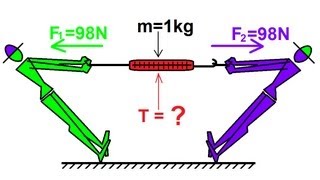
Physics 4 Newton's Laws of Motion (17 of 20) Third Law: Example 5
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! In this video I will explain the tension of the previous video using Newton's 3rd Law of motion.
From playlist PHYSICS - MECHANICS

Julius Sumner Miller Lesson 3: Newton's Second Law of Motion - The Elevator Problem
It is rather obvious that the greater the MASS - the greater the INERTIA of a body - the harder it is to put it into motion. That is: if a body of MASS M requires a FORCE F to give it "so much" motion - that is, so much acceleration - than a body of MASS 2M requires a FORCE 2F to give
From playlist Julius Sumner Miller - Full Physics Laboratory Demonstrations

Jorge Nocedal: "Tutorial on Optimization Methods for Machine Learning, Pt. 1"
Graduate Summer School 2012: Deep Learning, Feature Learning "Tutorial on Optimization Methods for Machine Learning, Pt. 1" Jorge Nocedal, Northwestern University Institute for Pure and Applied Mathematics, UCLA July 19, 2012 For more information: https://www.ipam.ucla.edu/programs/summ
From playlist GSS2012: Deep Learning, Feature Learning
Year 12/AS Mechanics Chapter 10.5 (Forces and Motion)
This lesson on the topic of Forces and Motion is centred on problems involving connected particles, or objects that can be modelled as particles. These can be questions where the particles are connected via a connecting material (eg a string, metal bar, rope etc) or the objects/particles
From playlist Year 12/AS Edexcel (8MA0) Mathematics: FULL COURSE

Lecture 16 | Convex Optimization I (Stanford)
Professor Stephen Boyd, of the Stanford University Electrical Engineering department, lectures on how equality constrained minimization is utilized in electrical engineering for the course, Convex Optimization I (EE 364A). Convex Optimization I concentrates on recognizing and solving co
From playlist Lecture Collection | Convex Optimization
MIT RES.TLL-004 STEM Concept Videos View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/RES-TLL-004F13 Instructor: Dan Hastings This video introduces the concept of the vector, explores vector properties using physical intuition based on displacements, and discusses how to recognize when a physi
From playlist MIT STEM Concept Videos

Newton's Laws of Motion - Physics 101 / AP Physics 1 Review - Dianna Cowern
Lesson 4 (Newton's Laws of Motion) of Dianna's Intro Physics Class on Physics Girl. Never taken physics before? Want to learn the basics of physics? Need an AP Physics 1 review before the exam? This course is for you! Exercises in this video: Problem 1: You push your square space cow, ma
From playlist Dianna's Intro Physics Class/ Physics 101/ AP Physics 1 Review with Physics Girl

This video covers Section 4.8 of Cutnell & Johnson Physics 10e, by David Young and Shane Stadler, published by John Wiley and Sons. The lecture is part of the course General Physics - Life Sciences I and II, taught by Dr. Boyd F. Edwards at Utah State University. This video was produced
From playlist Lecture 4B. Forces and Newton's Laws of Motion

From playlist Physics - Newton's law videos for analysis
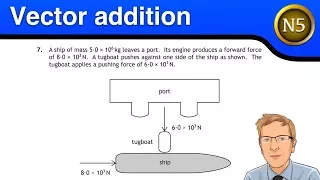
National 5 Physics - Vector addition
National 5 Physics - this video explains how to add vectors (i) by scale drawing and (ii) by calculation. ----------------------------------------------------- Support the channel – you can buy me a coffee here... https://www.buymeacoffee.com/MrSmith My Amazon storefront for school su
From playlist National 5 - Dynamics

This video tutorial lesson explains the meaning of the term weightlessness and identifies the cause of weightlessness. The variety of learner misconceptions associated with the topic are addressed. You can find more information that supports this video on our website: Lesson Notes: ht
From playlist Circular and Satellite Motion

From playlist Physics - Newton's law videos for analysis