Equidistant
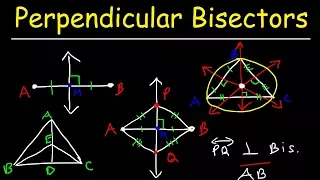
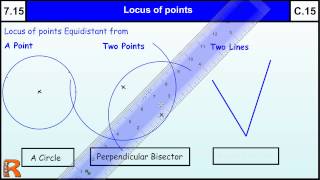
A point is said to be equidistant from a set of objects if the distances between that point and each object in the set are equal. In two-dimensional Euclidean geometry, the locus of points equidistant from two given (different) points is their perpendicular bisector. In three dimensions, the locus of points equidistant from two given points is a plane, and generalising further, in n-dimensional space the locus of points equidistant from two points in n-space is an (n−1)-space. For a triangle the circumcentre is a point equidistant from each of the three vertices. Every non-degenerate triangle has such a point. This result can be generalised to cyclic polygons: the circumcentre is equidistant from each of the vertices. Likewise, the incentre of a triangle or any other tangential polygon is equidistant from the points of tangency of the polygon's sides with the circle. Every point on a perpendicular bisector of the side of a triangle or other polygon is equidistant from the two vertices at the ends of that side. Every point on the bisector of an angle of any polygon is equidistant from the two sides that emanate from that angle. The center of a rectangle is equidistant from all four vertices, and it is equidistant from two opposite sides and also equidistant from the other two opposite sides. A point on the axis of symmetry of a kite is equidistant between two sides. The center of a circle is equidistant from every point on the circle. Likewise the center of a sphere is equidistant from every point on the sphere. A parabola is the set of points in a plane equidistant from a fixed point (the focus) and a fixed line (the directrix), where distance from the directrix is measured along a line perpendicular to the directrix. In shape analysis, the topological skeleton or medial axis of a shape is a thin version of that shape that is equidistant from its boundaries. In Euclidean geometry, parallel lines (lines that never intersect) are equidistant in the sense that the distance of any point on one line from the nearest point on the other line is the same for all points. In hyperbolic geometry the set of points that are equidistant from and on one side of a given line form a hypercycle (which is a curve not a line). (Wikipedia).