
Distance Between Two Vertices in Graphs | Graph Theory
What is the distance between two vertices in graph theory? We'll define vertex distance in graph theory, as well as defining graph geodiscs and graph diameter in today's lesson! The distance between two connected vertices is the length of a shortest path connecting them. The distance betw
From playlist Graph Theory
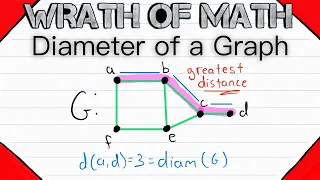
Diameter of a Graph | Graph Theory
What is the diameter of a graph in graph theory? This is a simple term we will define with examples in today's video graph theory lesson! Remember that the distance between two connected vertices in a graph is the length of a shortest path between those vertices. Here's my lesson on dist
From playlist Graph Theory
Graph Theory: 17. Distance Between Vertices and Connected Components
This video gives the definition of the distance between two vertices in a graph and explains what connected components are. --An introduction to Graph Theory by Dr. Sarada Herke. For quick videos about Math tips and useful facts, check out my other channel "Spoonful of Maths" - http://y
From playlist Graph Theory part-3

Graph Theory: 51. Eccentricity, Radius & Diameter
Eccentricity, radius and diameter are terms that are used often in graph theory. They are related to the concept of the distance between vertices. The distance between a pair of vertices is the length of a shortest path between them. We begin by reviewing some of the properties of dista
From playlist Graph Theory part-9
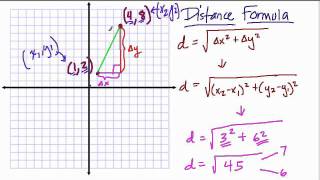
Distance Formula given a graph
An example using the distance formula when given a graph to analyze
From playlist Geometry

This video is about tournaments and some of their basic properties.
From playlist Basics: Graph Theory

"Find the distance between two points given their coordinates."
From playlist Algebra: Straight Line Graphs

Distance as a function -- Proofs
This lecture is on Introduction to Higher Mathematics (Proofs). For more see http://calculus123.com.
From playlist Proofs

What are Geodesics? | Graph Theory
What are geodesics in graph theory? We'll define them and give some examples in today's video graph theory lesson! And apologies for my mispronunciation and misspelling in this video. Remember that the distance between two connected vertices is the length of a shortest path connecting th
From playlist Graph Theory

What is the limit of a sequence of graphs?? | Benjamini-Schramm Convergence
This is an introduction to the mathematical concept of Benjamini-Schramm convergence, which is a type of graph limit theory which works well for sparse graphs. We hope that most of it is understandable by a wide audience with some mathematical background (including some prior exposure to g
From playlist Summer of Math Exposition Youtube Videos

Graphs are Metric Spaces | Graph Theory
We show that the vertex set of a graph, along with the standard vertex distance function, make a metric space by showing the distance between two vertices u and v satisfy the four necessary properties of a metric, including a proof of the triangle inequality property for the distance s bet
From playlist Graph Theory

Graph Diameter is Bounded by Radius | Graph Theory
We prove the diameter of a graph lies between the radius and two times the radius of the graph. This is a fun result which invokes some of the feeling of the classic d=2r formula from elementary geometry, and all it takes to prove is the triangle inequality! #graphtheory Graphs are Metri
From playlist Graph Theory
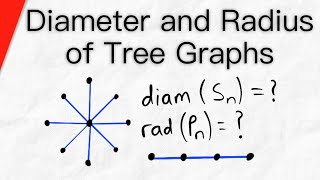
Diameter and Radius of Tree Graphs | Graph Theory
We discuss what family of tree graphs have maximum diameter, minimum diameter, maximum radius, and minimum radius. Recall the diameter of a graph is the maximum distance between any two vertices. The radius of a graph is the minimum eccentricity of any vertex. We'll find the star graphs ha
From playlist Graph Theory
Samplings and Observables. Limits of measured metric spaces - Gabor Elek
Conference on Graphs and Analysis Gabor Elek June 4, 2012 More videos on http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

Diameter and Radius of Graphs | Graph Theory
We define the radius of a graph and the diameter of a graph using the eccentricity of vertices. We relate these terms intuitively back to circles and discuss several examples of graph diameter and graph radius. We also introduce a theorem stating the diameter of a graph is bounded between
From playlist Graph Theory

Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Carnegie Mellon University is protecting the health and safety of its community by holding all large classes online. People from outside Carnegie Mellon University are welcome to tune in to see how the class is taught, but unfortunately Prof. Loh will not be o
From playlist CMU 21-228 Discrete Mathematics

Proof: Connected Graph Contains Two Non-Cut Vertices | Graph Theory, Connected Graphs
Every connected graph with at least two vertices contains two vertices (at least), that can be deleted without disconnecting the graph. Let's say our graph with at least two vertices is G. So there must be two vertices, say u and v, such that G-u and G-v are both connected. Thus, G contain
From playlist Graph Theory