Human-based units of measurement | Obsolete units of measurement | Units of length
Cubit
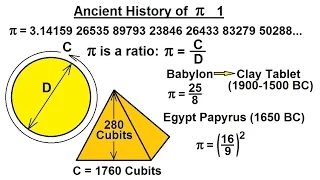
The cubit is an ancient unit of length based on the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger. It was primarily associated with the Sumerians, Egyptians, and Israelites. The term cubit is found in the Bible regarding Noah's Ark, Ark of the Covenant, Tabernacle, Solomon's Temple. The common cubit was divided into 6 palms × 4 fingers = 24 digits. Royal cubits added a palm for 7 palms × 4 fingers = 28 digits. These lengths typically ranged from 44.4 to 52.92 cm (1 ft 5+1⁄2 in to 1 ft 8+13⁄16 in), with an ancient Roman cubit being as long as 120 cm (3 ft 11 in). Cubits of various lengths were employed in many parts of the world in antiquity, during the Middle Ages and as recently as early modern times. The term is still used in hedgelaying, the length of the forearm being frequently used to determine the interval between stakes placed within the hedge. (Wikipedia).