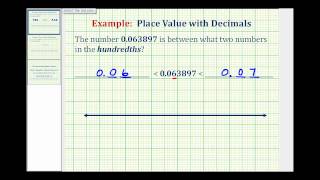
Ex 1: Determine What Two Decimals a Given Number is Between
This video provides and example of how to determine what a given number is between to specific place value Library: http://mathispower4u.com Search: http://mathispower4u.wordpress.com
From playlist Introduction to Decimals

Overview of Multiplicity of a zero - Online Tutor - Free Math Videos
👉 Learn about zeros and multiplicity. The zeroes of a polynomial expression are the values of x for which the graph of the function crosses the x-axis. They are the values of the variable for which the polynomial equals 0. The multiplicity of a zero of a polynomial expression is the number
From playlist Zeros and Multiplicity of Polynomials | Learn About

Overview of zeros of a polynomial - Online Tutor - Free Math Videos
👉 Learn about zeros and multiplicity. The zeroes of a polynomial expression are the values of x for which the graph of the function crosses the x-axis. They are the values of the variable for which the polynomial equals 0. The multiplicity of a zero of a polynomial expression is the number
From playlist Zeros and Multiplicity of Polynomials | Learn About

What is the multiplicity of a zero?
👉 Learn about zeros and multiplicity. The zeroes of a polynomial expression are the values of x for which the graph of the function crosses the x-axis. They are the values of the variable for which the polynomial equals 0. The multiplicity of a zero of a polynomial expression is the number
From playlist Zeros and Multiplicity of Polynomials | Learn About

Find the zeros factoring vs square root method
👉 Learn about zeros and multiplicity. The zeroes of a polynomial expression are the values of x for which the graph of the function crosses the x-axis. They are the values of the variable for which the polynomial equals 0. The multiplicity of a zero of a polynomial expression is the number
From playlist Zeros and Multiplicity of Polynomials | Learn About

What are zeros of a polynomial
👉 Learn about zeros and multiplicity. The zeroes of a polynomial expression are the values of x for which the graph of the function crosses the x-axis. They are the values of the variable for which the polynomial equals 0. The multiplicity of a zero of a polynomial expression is the number
From playlist Zeros and Multiplicity of Polynomials | Learn About

What is multiplicity and what does it mean for the zeros of a graph
👉 Learn about zeros and multiplicity. The zeroes of a polynomial expression are the values of x for which the graph of the function crosses the x-axis. They are the values of the variable for which the polynomial equals 0. The multiplicity of a zero of a polynomial expression is the number
From playlist Zeros and Multiplicity of Polynomials | Learn About

Overview Zeros of a functions - Online Math Tutor - Free Math Videos
👉 Learn about zeros and multiplicity. The zeroes of a polynomial expression are the values of x for which the graph of the function crosses the x-axis. They are the values of the variable for which the polynomial equals 0. The multiplicity of a zero of a polynomial expression is the number
From playlist Zeros and Multiplicity of Polynomials | Learn About

Learn how and why multiplicity of a zero make sense
👉 Learn about zeros and multiplicity. The zeroes of a polynomial expression are the values of x for which the graph of the function crosses the x-axis. They are the values of the variable for which the polynomial equals 0. The multiplicity of a zero of a polynomial expression is the number
From playlist Zeros and Multiplicity of Polynomials | Learn About

How we represent numbers in computers. Part of a larger series teaching programming. Visit codeschool.org Twitter: @brianwill
From playlist Numbers as bits

p-adic numbers. Part 2: p-adic powers
This is the second part of a 3-part talk on p-adic numbers for advanced high school students. It is part of a series organized by the Berkeley mathematics circle. We define the p-adic integers for p a prime, and use this to construct the field of p-adic numbers. We show how do do various
From playlist Math talks

Discrete Structures: Binary and Other Numbers Bases to Represent Data
In this video we'll learn about the base-2 number system, called binary. We'll learn how to convert numbers to and from binary. Then we'll extend our knowledge to other number bases, such as hexadecimal, base 32, and base 64. Finally we'll end with a discussion of how data is represented a
From playlist Discrete Structures, Spring 2022

Graphs of Exponential Functions (Precalculus - College Algebra 52)
Support: https://www.patreon.com/ProfessorLeonard Professor Leonard Merch: https://professor-leonard.myshopify.com An introduction to the graphs of exponential functions with a focus on why they look the way they do and how to identify key points and asymptotes.
From playlist Precalculus - College Algebra/Trigonometry

ELEC2141 Digital Circuit Design - Lecture 3
ELEC2141 Week 1 Lecture 3: Number Systems
From playlist ELEC2141 Digital Circuit Design
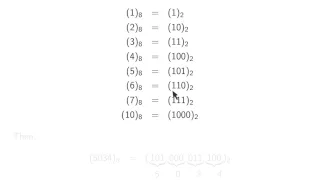
ch1 2: Representation of numbers in different bases. Wen Shen
Wen Shen, Penn State University. Lectures are based on my book: "An Introduction to Numerical Computation", published by World Scientific, 2016. See promo video: https://youtu.be/MgS33HcgA_I
From playlist CMPSC/MATH 451 Videos. Wen Shen, Penn State University

Discrete Structures: Floating-Point Representation and IEEE-754
In this session we'll learn how computers store floating-point numbers using a standard called IEEE-754. However, because the number of bits in the real standard is unwieldy, we will use a modified representation that uses fewer bits.
From playlist Discrete Structures, Spring 2022

Logarithm Fundamentals | Ep. 6 Lockdown live math
Back to the basics with logarithms. Full playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLZHQObOWTQDP5CVelJJ1bNDouqrAhVPev Home page: https://www.3blue1brown.com Brought to you by you: https://3b1b.co/ldm-thanks Triangle of power: https://youtu.be/sULa9Lc4pck Beautiful pictorial summary
From playlist Lockdown math

What do the zeros roots tell us of a polynomial
👉 Learn about zeros and multiplicity. The zeroes of a polynomial expression are the values of x for which the graph of the function crosses the x-axis. They are the values of the variable for which the polynomial equals 0. The multiplicity of a zero of a polynomial expression is the number
From playlist Zeros and Multiplicity of Polynomials | Learn About

Why 82,000 is an extraordinary number - Numberphile
Check out How Not To Be Wrong by Jordan Ellenberg: http://bit.ly/HowNotToBeWrong More links & stuff in full description below ↓↓↓ And special Kindle offer: http://bit.ly/Wrong_Special This video features Dr James Grime - http://singingbanana.com Cheers to Thomas Oléron Evans for inspir
From playlist James Grime on Numberphile
