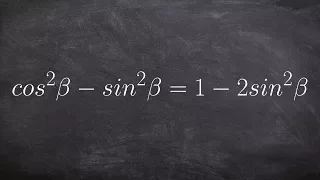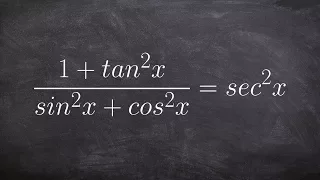Trihydrogen cation
The trihydrogen cation or protonated molecular hydrogen is a cation (positive ion) with formula H+3, consisting of three hydrogen nuclei (protons) sharing two electrons. The trihydrogen cation is one of the most abundant ions in the universe. It is stable in the interstellar medium (ISM) due to the low temperature and low density of interstellar space. The role that H+3 plays in the gas-phase chemistry of the ISM is unparalleled by any other molecular ion. The trihydrogen cation is the simplest triatomic molecule, because its two electrons are the only valence electrons in the system. It is also the simplest example of a three-center two-electron bond system. (Wikipedia).