
Covariance (1 of 17) What is Covariance? in Relation to Variance and Correlation
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! To donate:a http://www.ilectureonline.com/donate https://www.patreon.com/user?u=3236071 We will learn the difference between the variance and the covariance. A variance (s^2) is a measure of how spread out the numbers of
From playlist COVARIANCE AND VARIANCE

This educational video delves into how you quantify a linear statistical relationship between two variables using covariance! #statistics #probability #SoME2 This video gives a visual and intuitive introduction to the covariance, one of the ways we measure a linear statistical relation
From playlist Summer of Math Exposition 2 videos

Covariance Definition and Example
What is covariance? How do I find it? Step by step example of a solved covariance problem for a sample, along with an explanation of what the results mean and how it compares to correlation. 00:00 Overview 03:01 Positive, Negative, Zero Correlation 03:19 Covariance for a Sample Example
From playlist Correlation

Analysis of covariance using Python
This is the third video lecture in my seminar series on linear models. Here, I discuss analysis of covariance (ANCOVA). We combine what we have learned about linear regression and analysis of variance. In ANCOVA we have a categorical variable as independent variable and a continuous numer
From playlist Statistics
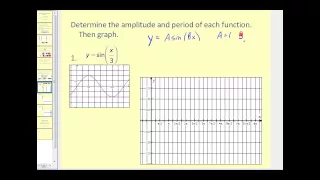
Amplitude and Period of Sine and Cosine
The video explains how to determine the amplitude and period of sine and cosine. It so graphs the functions with different amplitudes and periods. http://mathispower4u.wordpress.com/
From playlist Graphing Transformations of Trigonometric Functions

VARIABLES in Statistical Research (2-1)
A variable is any characteristic that can vary. An organized collection of numbers can be a variable. Qualitative variables indicate an attribute or belongingness to a category. Dichotomous variables are discrete variables that can have two and only two values. Quantitative variables indic
From playlist Forming Variables for Statistics & Statistical Software (WK 2 - QBA 237)

Estimation of Coherence and Cross Spectra
http://AllSignalProcessing.com for more great signal-processing content: ad-free videos, concept/screenshot files, quizzes, MATLAB and data files. Averaging approaches for estimating coherence and cross spectra, analogous to Welch's averaged periodogram estimator of the power spectrum.
From playlist Estimation and Detection Theory

RELATIONSHIPS Between Variables: Standardized Covariance (7-1)
Correlation is a way of measuring the extent to which two variables are related. The term correlation is synonymous with “relationship.” Variables are related when changes in one variable are consistently associated with changes in another variable. Dr. Daniel reviews Variance, Covariance,
From playlist Correlation And Regression in Statistics (WK 07 - QBA 237)

Discovering Variables – Combining Numbers for More Powerful Statistics (1-4)
Combining numbers creates variables – values that can vary or take on more than one value. If a value can be measured among a group and that value will be different for at least some of the group members, then you are measuring a variable. You will learn about qualitative (categorical) and
From playlist WK1 Numbers and Variables - Online Statistics for the Flipped Classroom
Einstein's General Theory of Relativity | Lecture 5
Lecture 5 of Leonard Susskind's Modern Physics concentrating on General Relativity. Recorded October 20, 2008 at Stanford University. This Stanford Continuing Studies course is the fourth of a six-quarter sequence of classes exploring the essential theoretical foundations of modern phys
From playlist Lecture Collection | Modern Physics: Einstein's Theory

R - SEM - Latent (Growth) Curve Modeling Class Assignment
Recorded: Summer 2015 Lecturer: Dr. Erin M. Buchanan Packages needed: lavaan, semPlot Class assignment for structural equation modeling. Topic covers how program different types of latent curve models (linear only) including fit indices, random slopes and intercepts, and their interpretat
From playlist Structural Equation Modeling
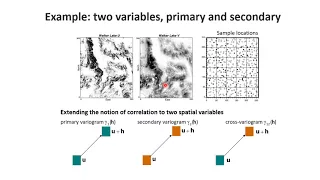
Geostatistics session 6 multi-variate
Introduction to co-kriging and co-simulation
From playlist Geostatistics GS240
Statistical Rethinking 2022 Lecture 16 - Gaussian Processes
Slides and other course materials: https://github.com/rmcelreath/stat_rethinking_2022 Intro: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uYNzqgU7na4 Music: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kXuasY8pDpA Music: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eTtTB0nZdL0 Pause: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pxPdsqrQByM
From playlist Statistical Rethinking 2022

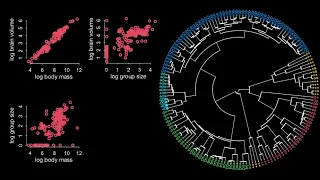
Statistical Rethinking 2023 - 16 - Gaussian Processes
Course: https://github.com/rmcelreath/stat_rethinking_2023 Intro music: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_3XGEsDSInM Outline 00:00 Introduction 02:37 Oceanic spatial confounds 09:54 Gaussian processes 24:26 Oceanic Gaussian process 33:51 Pause 34:37 Phylogenetic regression 1:18:39 Summary
From playlist Statistical Rethinking 2023

Statistical Rethinking Winter 2019 Lecture 17
Lecture 17 of the Dec 2018 through March 2019 edition of Statistical Rethinking: A Bayesian Course with R and Stan. Introduction to varying slopes and covariance priors.
From playlist Statistical Rethinking Winter 2019

Michael Bertolacci - AdaptSPEC-X: Spectral analysis of multiple non stationary time series
Dr Michael Bertolacci (University of Wollongong) presents “AdaptSPEC-X: Spectral analysis of multiple non stationary time series”, 08/10/2020. Seminar organised by ANU.
From playlist Statistics Across Campuses
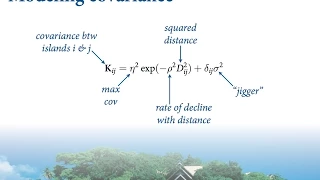
Statistical Rethinking - Lecture 19
Lecture 19 - Gaussian processes, measurement error - Statistical Rethinking: A Bayesian Course with R Examples
From playlist Statistical Rethinking Winter 2015

Statistical Rethinking Fall 2017 - week09 lecture16
Week 09, lecture 16 for Statistical Rethinking: A Bayesian Course with Examples in R and Stan, taught at MPI-EVA in Fall 2017. This lecture covers Chapter 13. Slides are available here: https://speakerdeck.com/rmcelreath/statistical-rethinking-fall-2017-lecture-16 Additional informatio
From playlist Statistical Rethinking Fall 2017

Statistical Rethinking Fall 2017 - week09 lecture17
Week 09, lecture 17 for Statistical Rethinking: A Bayesian Course with Examples in R and Stan, taught at MPI-EVA in Fall 2017. This lecture covers Chapter 13. Slides are available here: https://speakerdeck.com/rmcelreath/statistical-rethinking-fall-2017-lecture-17 Additional informatio
From playlist Statistical Rethinking Fall 2017
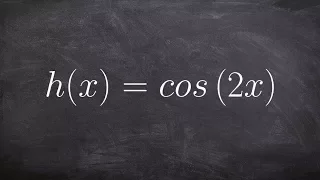
Graphing the Cosine Function with a Change in the Period
👉 Learn how to graph a cosine function. To graph a cosine function, we first determine the amplitude (the maximum point on the graph), the period (the distance/time for a complete oscillation), the phase shift (the horizontal shift from the parent function), the vertical shift (the vertica
From playlist How to Graph Trigonometric Functions