Articles containing proofs | Theorems in real analysis | Theorems in calculus | Approximations
Taylor's theorem
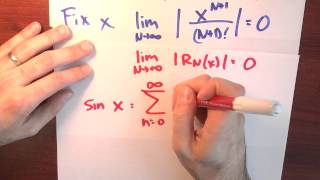
In calculus, Taylor's theorem gives an approximation of a k-times differentiable function around a given point by a polynomial of degree k, called the kth-order Taylor polynomial. For a smooth function, the Taylor polynomial is the truncation at the order k of the Taylor series of the function. The first-order Taylor polynomial is the linear approximation of the function, and the second-order Taylor polynomial is often referred to as the quadratic approximation. There are several versions of Taylor's theorem, some giving explicit estimates of the approximation error of the function by its Taylor polynomial. Taylor's theorem is named after the mathematician Brook Taylor, who stated a version of it in 1715, although an earlier version of the result was already mentioned in 1671 by James Gregory. Taylor's theorem is taught in introductory-level calculus courses and is one of the central elementary tools in mathematical analysis. It gives simple arithmetic formulas to accurately compute values of many transcendental functions such as the exponential function and trigonometric functions.It is the starting point of the study of analytic functions, and is fundamental in various areas of mathematics, as well as in numerical analysis and mathematical physics. Taylor's theorem also generalizes to multivariate and vector valued functions. (Wikipedia).