
Find the Cost Function given the Marginal Cost and Fixed Costs
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!! https://goo.gl/JQ8Nys Find the Cost Function given the Marginal Cost and Fixed Costs
From playlist Calculus

Ex 1: Cost Function Applications - Marginal Cost, Average Cost, Minimum Average Cost
This video explains how several application of the cost function including total cost, marginal cost, average cost, and minimum average cost. The total cost function is a quadratic function. Site: http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Applications of Differentiation – Maximum/Minimum/Optimization Problems

In this video we cover the idea of marginal cost. This is simply the derivative of the cost function. We can roughly define marginal cost as the cost of producing one additional item. For more videos please visit http://www.mysecretmathtutor.com
From playlist Calculus

Ex: Find the Average Cost Function and Minimize the Average Cost
This video explains how to find the average cost function and find the minimum average cost given the total cost function. Site: http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Applications of Differentiation – Maximum/Minimum/Optimization Problems

Percentage Increase & Decrease - Using Multipliers | Number | Maths | FuseSchool
In this video we are going to look at how to do percentage increases and decreases, using multipliers. You should already know what percentages are, and how to find them. Example: A train ticket costing £40 is reduced by 20%. What is the price of the new ticket? 20% of 40 = 20/100 X 40
From playlist MATHS: Numbers

Ex 2: Cost Function Applications - Marginal Cost, Average Cost, Minimum Average Cost
This video explains how several application of the cost function including total cost, marginal cost, average cost, and minimum average cost. The total cost function is a quadratic function. Site: http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Applications of Differentiation – Maximum/Minimum/Optimization Problems

How Much Should I Spend on a Car?
In this video I talk about what a reasonable upper limit is for most people when it comes to cars. How much should you spend on a car? I answer this question and share my thoughts.
From playlist Finance

Finding the Marginal Cost Function given the Cost Function
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!! https://goo.gl/JQ8Nys Finding the Marginal Cost Function given the Cost Function
From playlist Calculus
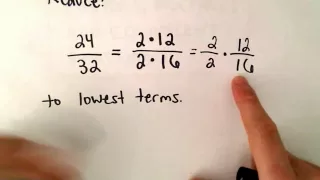
Reducing a Fraction to Lowest Terms
Thanks to all of you who support me on Patreon. You da real mvps! $1 per month helps!! :) https://www.patreon.com/patrickjmt !! Reducing a Fraction to Lowest Terms. Here I look at reducing a fraction to lowest terms. I do not take the shortest route, but show how I often perform the s
From playlist All Videos - Part 2

MongoDB Tutorial 4 Map Reduce Finalize Group
Get the Code Here : http://goo.gl/vpPjSP Best MongoDB Book : http://amzn.to/1VdclfA I received a bunch of questions about using Map Reduce in MongoDB, so here I provide a bunch of examples. First I'll cover Map Reduce using straight JavaScript. Then we'll cover increasingly complex MongoD
From playlist NodeJS Tutorial

Creating Value with Risk Management - Financial Risk Manager | Simplilearn
🔥Explore Our Free Courses With Completion Certificate by SkillUp: https://www.simplilearn.com/skillup-free-online-courses?utm_campaign=CreatingValuewithRiskManagement&utm_medium=DescriptionFirstFold&utm_source=youtube This video explains the: 1.Reducing Bankruptcy Costs 2.Reducing Taxable
From playlist FRM Tutorial | Financial Risk Management Tutorial | Simplilearn

DDPS | Learning hierarchies of reduced-dimension and context-aware models for Monte Carlo sampling
In this DDPS Seminar Series talk from Sept. 2, 2021, University of Texas at Austin postdoctoral fellow Ionut-Gabriel Farcas discusses hierarchies of reduced-dimension and context-aware low-fidelity models for multi-fidelity Monte Carlo sampling. Description: In traditional model reduction
From playlist Data-driven Physical Simulations (DDPS) Seminar Series

OSCON 2010: Mark Masterson, "Is the Enterprise Ready for the Cloud?"
http://oscon.com Mark Masterson (CSC) , "Is the Enterprise Ready for the Cloud?"
From playlist OSCON 10 Cloud Summit

Ses 2-4 | MIT 16.660 Introduction to Lean Six Sigma Methods, January (IAP) 2008
Session 2-4: Lean engineering basics License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT 16.660 Introduction to Lean Six Sigma Methods, IAP 2008

DDPS | Cheap and robust adaptive reduced order models for nonlinear inversion and design
Description: Nonlinear inverse problems and other PDE-constrained optimization problems, such as structural design under many load cases, require the repeated solution of many discretized large linear systems (or nonlinear systems). For Newton-type methods we also need solutions for the ad
From playlist Data-driven Physical Simulations (DDPS) Seminar Series
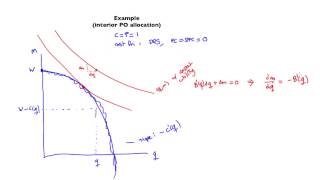
Unit 5 - pareto optimal allocations part 4
From playlist Courses and Series



