
Solving using the quadratic formula
👉 Learn how to solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest power on its variable(s) is 2. The quadratic formula is a formula which can be used to find the roots of (solve) a quadratic equation. The quadratic formula is given by
From playlist Solve by Quadratic Formula With Missing Terms

Michael Kerber (12/08/2021): Multi-Parameter Persistent Homology is Practical
Abstract: Multi-parameter persistent homology is an active research branch of topological data analysis. Early work has mainly focused on the theoretical part of the area, leaving the links to application area underdeveloped. One reason for this imbalance is the difficulty of computing the
From playlist AATRN 2021

CS25 I Stanford Seminar - DeepMind's Perceiver and Perceiver IO: new data family architecture
A central goal of artificial intelligence is to build systems that can flexibly process all the world's data, but current neural network architectures are designed to handle essentially one data configuration. This includes models like 2D convnets and more recent Vision Transformer models,
From playlist Stanford Seminars

Deeper Combinatorial Lower Bounds - Siu Man Chan
Siu Man Chan Princeton University January 21, 2014 We will discuss space and parallel complexity, ranging from some classical results which motivated the study, to some recent results concerning combinatorial lower bounds in restricted settings. We will highlight some of their connections
From playlist Mathematics

Teresa Heiss (9/23/21): Geometry and Topology of Periodic Point Sets, for example Crystals
My talk will consist of two parts. Firstly, I will explain how tools of Computational Geometry and Topology, like Brillouin zones and order k persistent homology, can help in a material science application, namely in finding so-called crystal fingerprints that characterize crystalline mate
From playlist AATRN 2021
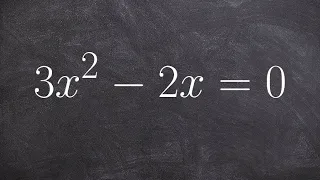
Solve by using the quadratic formula
👉 Learn how to solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest power on its variable(s) is 2. The quadratic formula is a formula which can be used to find the roots of (solve) a quadratic equation. The quadratic formula is given by
From playlist Solve by Quadratic Formula With Missing Terms
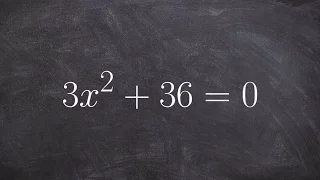
Learn how to solve using quadratic formula
👉 Learn how to solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest power on its variable(s) is 2. The quadratic formula is a formula which can be used to find the roots of (solve) a quadratic equation. The quadratic formula is given by
From playlist Solve by Quadratic Formula With Missing Terms

Perceiver: General Perception with Iterative Attention (Google DeepMind Research Paper Explained)
#perceiver #deepmind #transformer Inspired by the fact that biological creatures attend to multiple modalities at the same time, DeepMind releases its new Perceiver model. Based on the Transformer architecture, the Perceiver makes no assumptions on the modality of the input data and also
From playlist Papers Explained

GShard: Scaling Giant Models with Conditional Computation and Automatic Sharding (Paper Explained)
Google builds a 600 billion parameter transformer to do massively multilingual, massive machine translation. Interestingly, the larger model scale does not come from increasing depth of the transformer, but from increasing width in the feedforward layers, combined with a hard routing to pa
From playlist Papers Explained

Jeff Erickson - Lecture 4 - Two-dimensional computational topology - 21/06/18
School on Low-Dimensional Geometry and Topology: Discrete and Algorithmic Aspects (http://geomschool2018.univ-mlv.fr/) Jeff Erickson (University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA) Two-dimensional computational topology - Lecture 4 Abstract: This series of lectures will describe recent
From playlist Jeff Erickson - School on Low-Dimensional Geometry and Topology: Discrete and Algorithmic Aspects

The discriminant and finding the solutions using quadratic formula
👉 Learn how to solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest power on its variable(s) is 2. The quadratic formula is a formula which can be used to find the roots of (solve) a quadratic equation. The quadratic formula is given by
From playlist Solve by Quadratic Formula | x^2+bx+c

Solve a quadratic equation using the quadratic formula when their are imaginary solutions
👉 Learn how to solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest power on its variable(s) is 2. The quadratic formula is a formula which can be used to find the roots of (solve) a quadratic equation. The quadratic formula is given by
From playlist Solve by Quadratic Formula | ax^2+bx+c

Learning to solve a quadratic with two irrational solutions using quadratic formula
👉 Learn how to solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest power on its variable(s) is 2. The quadratic formula is a formula which can be used to find the roots of (solve) a quadratic equation. The quadratic formula is given by
From playlist Solve by Quadratic Formula | Equation

Learn to find the zeros of a quadratic using the quadratic formula
👉 Learn how to solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest power on its variable(s) is 2. The quadratic formula is a formula which can be used to find the roots of (solve) a quadratic equation. The quadratic formula is given by
From playlist Solve by Quadratic Formula | Equation

Solving a quadratic by applying the quadratic formula
👉 Learn how to solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest power on its variable(s) is 2. The quadratic formula is a formula which can be used to find the roots of (solve) a quadratic equation. The quadratic formula is given by
From playlist Solve by Quadratic Formula | x^2+bx+c
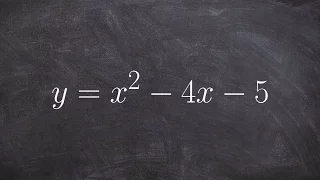
Solving a quadratic by applying the quadratic formula
👉 Learn how to solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest power on its variable(s) is 2. The quadratic formula is a formula which can be used to find the roots of (solve) a quadratic equation. The quadratic formula is given by
From playlist Solve by Quadratic Formula | x^2+bx+c

AQC 2016 - Quantum Monte Carlo vs Tunneling vs. Adiabatic Optimization
A Google TechTalk, June 27, 2016, presented by Aram Harrow (MIT) ABSTRACT: Can quantum adiabatic evolution solve optimization problems much faster than classical computers? One piece of evidence for this has been their apparent advantage in "tunneling" through barriers to escape local mi
From playlist Adiabatic Quantum Computing Conference 2016
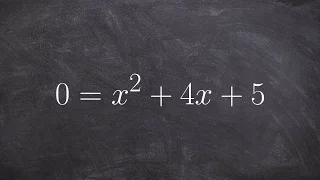
Solving a quadratic by applying the quadratic formula
👉 Learn how to solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. A quadratic equation is an equation whose highest power on its variable(s) is 2. The quadratic formula is a formula which can be used to find the roots of (solve) a quadratic equation. The quadratic formula is given by
From playlist Solve by Quadratic Formula | x^2+bx+c

