Articles containing proofs | Theorems about quadrilaterals and circles | Euclidean plane geometry
Ptolemy's theorem
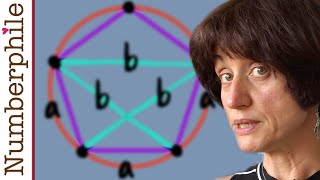
In Euclidean geometry, Ptolemy's theorem is a relation between the four sides and two diagonals of a cyclic quadrilateral (a quadrilateral whose vertices lie on a common circle). The theorem is named after the Greek astronomer and mathematician Ptolemy (Claudius Ptolemaeus). Ptolemy used the theorem as an aid to creating his table of chords, a trigonometric table that he applied to astronomy. If the vertices of the cyclic quadrilateral are A, B, C, and D in order, then the theorem states that: where the vertical lines denote the lengths of the line segments between the named vertices. This relation may be verbally expressed as follows: If a quadrilateral is inscribable in a circle then the product of the lengths of its diagonals is equal to the sum of the products of the lengths of the pairs of opposite sides. Moreover, the converse of Ptolemy's theorem is also true: In a quadrilateral, if the sum of the products of the lengths of its two pairs of opposite sides is equal to the product of the lengths of its diagonals, then the quadrilateral can be inscribed in a circle i.e. it is a cyclic quadrilateral. (Wikipedia).