
Introductory talk on series. Defining a series as a sequence of partial sums.
From playlist Advanced Calculus / Multivariable Calculus
Example and looking ahead at methods of calculating convergence.
From playlist Advanced Calculus / Multivariable Calculus

Calculus 2 Lecture 8.1: Solving First Order Differential Equations By Separation of Variables
Calculus 2 Lecture 8.1: Solving First Order Differential Equations By Separation of Variables
From playlist Calculus 2 (Full Length Videos)

3_4 Example Problems Involving Series
Example problems.
From playlist Advanced Calculus / Multivariable Calculus

Calculus 1 Lecture 4.2: Integration by Substitution
Calculus 1 Lecture 4.2: Integration by Substitution
From playlist Calculus 1 (Full Length Videos)
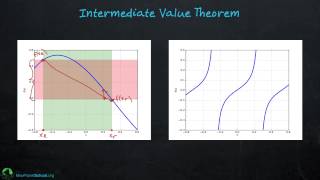
Calculus: Bisection, Secant, and Newton
This video provides a unique view into what Calculus is, what it can be used for, and how it can be used in the real world. To illustrate how these three concepts are all connected, I consider the two very important examples of finding the solution of a complicated equation and finding the
From playlist Calculus

Calculus 1 Lecture 2.6: Discussion of the Chain Rule for Derivatives of Functions
Calculus 1 Lecture 2.6: Discussion of the Chain Rule for Derivatives of Functions
From playlist Calculus 1 (Full Length Videos)

11_3_1 The Gradient of a Multivariable Function
Using the partial derivatives of a multivariable function to construct its gradient vector.
From playlist Advanced Calculus / Multivariable Calculus

Calculus 1 Lecture 3.1: Increasing/Decreasing and Concavity of Functions
Calculus 1 Lecture 3.1: Discussion of Increasing and Decreasing Intervals. Discussion of Concavity of functions.
From playlist Calculus 1 (Full Length Videos)

Stochastic density functional theory....(Lecture 01) by David Dean
ORGANIZERS: Abhishek Dhar and Sanjib Sabhapandit DATE: 27 June 2018 to 13 July 2018 VENUE: Ramanujan Lecture Hall, ICTS Bangalore This advanced level school is the ninth in the series. This is a pedagogical school, aimed at bridging the gap between masters-level courses and topics in
From playlist Bangalore School on Statistical Physics - IX (2018)

Machine Learning from First Principles, with PyTorch AutoDiff — Topic 66 of ML Foundations
#MLFoundations #Calculus #MachineLearning In preceding videos in this series, we learned all the most essential differential calculus theory needed for machine learning. In this epic video, it all comes together to enable us to perform machine learning from first principles and fit a line
From playlist Calculus for Machine Learning

Lambda Calculus - Computerphile
The basis of almost all functional programming, Professor Graham Hutton explains Lambda Calculus. http://www.facebook.com/computerphile https://twitter.com/computer_phile This video was filmed and edited by Sean Riley. Computer Science at the University of Nottingham: http://bit.ly/nott
From playlist Subtitled Films

First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Calculus 1 AB
I introduce and define the First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. I finish by working through 4 examples involving Polynomials, Quotients, Radicals, Absolute Value Function, and Trigonometric Functions. Check out http://www.ProfRobBob.com, there you will find my lessons organized by clas
From playlist Calculus

Calculus made easy, the Mathologer way :) 00:00 Intro 00:49 Calculus made easy. Silvanus P. Thompson comes alive 03:12 Part 1: Car calculus 12:05 Part 2: Differential calculus, elementary functions 19:08 Part 3: Integral calculus 27:21 Part 4: Leibniz magic notation 30:02 Animations: prod
From playlist Recent videos

4. Calculus: One of the Most Successful Technologies
(October 22, 2012) Professor Keith Devlin discusses how calculus is truly one of the most useful discoveries of all time. Originally presented in the Stanford Continuing Studies Program. Stanford University: http://www.stanford.edu/ Stanford Continuing Studies Program: https://continuin
From playlist Lecture Collection | Mathematics: Making the Invisible Visible
Toward Computer-Based Calculus
In this Wolfram Technology Conference talk, Nikolay Brodskiy shares his experiences with using Wolfram technologies, including Mathematica and Wolfram|Alpha, for a computer-based approach to teaching calculus. For more information about Mathematica, please visit: http://www.wolfram.com/ma
From playlist Wolfram Technology Conference 2012

Pre-Calculus - The vocabulary of linear functions and equations
This video will introduce you to a few of the terms that are commonly used with linear functions and equations. Pay close attention to how you can tell the difference between linear and non-linear functions. For more videos please visit http://www.mysecretmathtutor.com
From playlist Pre-Calculus


