
Linear Algebra for Computer Scientists. 12. Introducing the Matrix
This computer science video is one of a series of lessons about linear algebra for computer scientists. This video introduces the concept of a matrix. A matrix is a rectangular or square, two dimensional array of numbers, symbols, or expressions. A matrix is also classed a second order
From playlist Linear Algebra for Computer Scientists

What is a matrix? Free ebook http://tinyurl.com/EngMathYT
From playlist Intro to Matrices

We have already looked at the column view of a matrix. In this video lecture I want to expand on this topic to show you that each matrix has a column space. If a matrix is part of a linear system then a linear combination of the columns creates a column space. The vector created by the
From playlist Introducing linear algebra

11_7_1 Potential Function of a Vector Field Part 1
The gradient of a function is a vector. n-Dimensional space can be filled up with countless vectors as values as inserted into a gradient function. This is then referred to as a vector field. Some vector fields have potential functions. In this video we start to look at how to calculat
From playlist Advanced Calculus / Multivariable Calculus

Introduction to Vector Fields This video discusses, 1) The definition of a vector field. 2) Examples of vector fields including the gradient, and various velocity fields. 3) The definition of a conservative vector field. 4) The definition of a potential function. 5) Test for conservative
From playlist Calculus 3
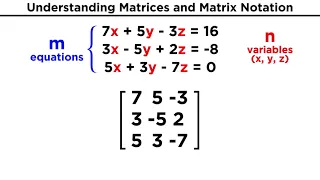
Understanding Matrices and Matrix Notation
In order to do linear algebra, we will have to know how to use matrices. So what's a matrix? It's just an array of numbers listed in a grid of particular dimensions that can represent the coefficients and constants from a system of linear equations. They're fun, I promise! Let's just start
From playlist Mathematics (All Of It)

Matrix Representations of Fields - Lecture 04 - Field Theory
For a finite extension K of F of degree d there exists a ring map from K to d x d matrices with entries in F which is injective. This allows us to define the norm, trace, and characteristic polynomial of an element. The minimal polynomial of this associated matrix is the minimal polynomial
From playlist Field Theory

Worldwide Calculus: Vector Fields
Lecture on 'Vector Fields' from 'Worldwide Multivariable Calculus'. For more lecture videos and $10 digital textbooks, visit www.centerofmath.org.
From playlist Integration and Vector Fields

Lecture 5 (CEM) -- TMM Using Scattering Matrices
This lecture formulates a stable transfer matrix method based on scattering matrices. The scattering matrices adopted here are greatly improved from the literature and are consistent with convention. The lecture ends with some advanced topics like dispersion analysis, cascading and doubl
From playlist UT El Paso: CEM Lectures | CosmoLearning.org Electrical Engineering

An algebraic algorithm for non-commutative rank over any field - K.V. Subrahmanyam
Optimization, Complexity and Invariant Theory Topic: An algebraic algorithm for non-commutative rank over any field Speaker: K.V. Subrahmanyam Affiliation: Chennai Mathematical Institute Date: June 6. 2018 For more videos, please visit http://video.ias.edu
From playlist Mathematics

Lecture 19 (CEM) -- Formulation of Rigorous Coupled-Wave Analysis
This lecture steps the student through the formulation of rigorous coupled-wave analysis. It parallels the lecture on the transfer matrix method and adopts the same formalism for scattering matrices. A bonus section discusses the enhanced transmittance matrix approach. Prerequisite Lect
From playlist UT El Paso: CEM Lectures | CosmoLearning.org Electrical Engineering

Lecture 23 (CEM) -- Slice Absorption Method
This lecture introduces the student to the slice absorption method, which is essentially a block tridiagonal solver for the finite-difference frequency-domain method. It is able to solve larger problems than the conventional finite-difference frequency-domain method. Prerequisite Lecture
From playlist UT El Paso: CEM Lectures | CosmoLearning.org Electrical Engineering

RubyConf 2015 - Not so Neo In the Matrix by Micah Adams
Not so Neo In the Matrix by Micah Adams Matrices are powerful data structures that are used for all sorts of interesting problems- from 3d graphics, to image processing, and cryptography. However, the mighty matrix can be used to solve more mundane problems as well. This talk attempts to
From playlist RubyConf 2015

[Lesson 23] QED Prerequisites: The moving dipole
The purpose of this lesson is simply to exercise the transformation of the electromagnetic field tensor using the formalism of Jackson. To do this we pose the problem of the transformation of the magnetic field of a moving magnetic dipole. Much of this paper was drawn from the following pa
From playlist QED- Prerequisite Topics

Linear Algebra - Vector Spaces and Linear Maps: Oxford Mathematics 2nd Year Student Lecture
The latest in our series of lectures is the first lecture in Alan Lauder's Second Year Linear Algebra Course. In this lecture Alan (with help from Cosi) explains to students how the course will unfold before going on to talk specifically about Vector Spaces and Linear Maps. You can watch
From playlist Oxford Mathematics Student Lectures - Linear Algebra

Lecture 12 (CEM) -- Formulation of Finite-Difference Frequency-Domain
This lecture steps the student through the formulation of the finite-difference frequency-domain model. Many concepts from previous lectures come together in this formulation. Prerequisite Lectures: 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, and 9
From playlist UT El Paso: CEM Lectures | CosmoLearning.org Electrical Engineering

12. Atoms in External Fields IV and Atom-light Interactions I
MIT 8.421 Atomic and Optical Physics I, Spring 2014 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/8-421S14 Instructor: Wolfgang Ketterle In this lecture, the professor discussed index of refraction and started to talk about atom-light Interactions. License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More
From playlist MIT 8.421 Atomic and Optical Physics I, Spring 2014

Calculus 3 Lecture 15.1: INTRODUCTION to Vector Fields (and what makes them Conservative)
Calculus 3 Lecture 15.1: INTRODUCTION to Vector Fields (and what makes them Conservative): What Vector Fields are, and what they look like. We discuss graphing Vector Fields in 2-D and 3-D and talk about what a Conservative Vector Field means.
From playlist Calculus 3 (Full Length Videos)

Tobias Braun - Orthogonal Determinants
Basic concepts and notions of orthogonal representations are in- troduced. If X : G → GL(V ) is a K-representation of a nite group G it may happen that its image X(G) xes a non-degenerate quadratic form q on V . In this case X and its character χ : G → K, g 7 → trace(X(g)) are called ortho
From playlist École d'Été 2022 - Cohomology Geometry and Explicit Number Theory

Matrix Algebra Basics || Matrix Algebra for Beginners
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array or table of numbers, symbols, or expressions, arranged in rows and columns. This course is about basics of matrix algebra. Website: https://geekslesson.com/ 0:00 Introduction 0:19 Vectors and Matrices 3:30 Identities and Transposes 5:59 Add
From playlist Algebra