
Ex: Determine the Value of a Number on a Logarithmic Scale (Log Form)
This video explains how to determine the value of several numbers on a logarithmic scale scaled in logarithmic form. http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Using the Definition of a Logarithm

Solving the Logarithmic Equation log(A) = log(B) - C*log(x) for A
Solving the Logarithmic Equation log(A) = log(B) - C*log(x) for A Please Subscribe here, thank you!!! https://goo.gl/JQ8Nys
From playlist Logarithmic Equations

Solving a natural logarithmic equation using your calculator
👉 Learn how to solve logarithmic equations. Logarithmic equations are equations with logarithms in them. To solve a logarithmic equation, we first isolate the logarithm part of the equation. After we have isolated the logarithm part of the equation, we then get rid of the logarithm. This i
From playlist Solve Logarithmic Equations

Algebra Ch.47: Logarithmic Functions (3 of 26) Why do We Need Logarithmic Functions?
Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures! To donate: http://www.ilectureonline.com/donate https://www.patreon.com/user?u=3236071 We will learn why in the world do we even need logarithmic functions: 1) We need it to solve for sound in decibels (dB). 2) We need i
From playlist ALGEBRA CH 47 LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
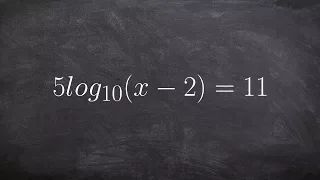
Solving a logarithmic equation by using inverse properties
👉 Learn how to solve logarithmic equations. Logarithmic equations are equations with logarithms in them. To solve a logarithmic equation, we first isolate the logarithm part of the equation. After we have isolated the logarithm part of the equation, we then get rid of the logarithm. This i
From playlist Solve Logarithmic Equations
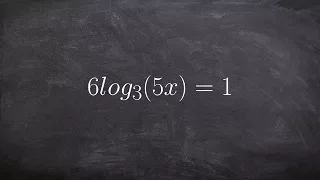
Solving a logarithmic equation in two different ways
👉 Learn how to solve logarithmic equations. Logarithmic equations are equations with logarithms in them. To solve a logarithmic equation, we first isolate the logarithm part of the equation. After we have isolated the logarithm part of the equation, we then get rid of the logarithm. This i
From playlist Solve Logarithmic Equations

Using inverse operation to solve a natural logarithmic equation
👉 Learn how to solve logarithmic equations. Logarithmic equations are equations with logarithms in them. To solve a logarithmic equation, we first isolate the logarithm part of the equation. After we have isolated the logarithm part of the equation, we then get rid of the logarithm. This i
From playlist Solve Logarithmic Equations
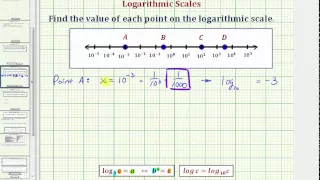
Ex: Determine the Value of a Number on a Logarithmic Scale (Exponential Form)
This video explains how to determine the value of several numbers on a logarithmic scale scaled in exponential form. http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Using the Definition of a Logarithm

Lecture 3 | Modern Physics: Statistical Mechanics
April 13, 2009 - Leonard Susskind reviews the Lagrange multiplier, explains Boltzmann distribution and Helm-Holtz free energy before oulining into the theory of fluctuations. Stanford University: http://www.stanford.edu/ Stanford Continuing Studies Program: http://csp.stanford.edu/
From playlist Lecture Collection | Modern Physics: Statistical Mechanics

Physical chemistry is the study of macroscopic, and particulate phenomena in chemical systems in terms of the principles, practices, and concepts of physics such as motion, energy, force, time, #thermodynamics, #quantum chemistry, #statistical mechanics, analytical dynamics and chemical eq
From playlist Physical Chemistry

Multi-mode Correlations in Turbulence by Gregory Falkovich
PROGRAM TURBULENCE: PROBLEMS AT THE INTERFACE OF MATHEMATICS AND PHYSICS ORGANIZERS: Uriel Frisch (Observatoire de la Côte d'Azur and CNRS, France), Konstantin Khanin (University of Toronto, Canada) and Rahul Pandit (IISc, India) DATE: 16 January 2023 to 27 January 2023 VENUE: Ramanuja
From playlist Turbulence: Problems at the Interface of Mathematics and Physics 2023

Lecture 1 | Modern Physics: Statistical Mechanics
March 30, 2009 - Leonard Susskind discusses the study of statistical analysis as calculating the probability of things subject to the constraints of a conserved quantity. Susskind introduces energy, entropy, temperature, and phase states as they relate directly to statistical mechanics.
From playlist Lecture Collection | Modern Physics: Statistical Mechanics

Math tutorial for solving logarithmic equation using inverse operations
👉 Learn how to solve logarithmic equations. Logarithmic equations are equations with logarithms in them. To solve a logarithmic equation, we first isolate the logarithm part of the equation. After we have isolated the logarithm part of the equation, we then get rid of the logarithm. This i
From playlist Solve Logarithmic Equations

Statistical Mechanics Lecture 3
(April 15, 20123) Leonard Susskind begins the derivation of the distribution of energy states that represents maximum entropy in a system at equilibrium. Originally presented in the Stanford Continuing Studies Program. Stanford University: http://www.stanford.edu/ Continuing Studies P
From playlist Course | Statistical Mechanics

Lecture 7 | Quantum Entanglements, Part 1 (Stanford)
Lecture 7 of Leonard Susskind's course concentrating on Quantum Entanglements (Part 1, Fall 2006). Recorded November 6, 2006 at Stanford University. This Stanford Continuing Studies course is the first of a three-quarter sequence of classes exploring the "quantum entanglements" in moder
From playlist Course | Quantum Entanglements: Part 1 (Fall 2006)

Statistical Mechanics Lecture 4
(April 23, 2013) Leonard Susskind completes the derivation of the Boltzman distribution of states of a system. This distribution describes a system in equilibrium and with maximum entropy. Originally presented in the Stanford Continuing Studies Program. Stanford University: http://www.st
From playlist Course | Statistical Mechanics

Disorder-generated multifractals and random matrices: freezing phenomena and extremes - Yan Fyodorov
Yan Fyodorov Queen Mary University of London October 3, 2013 I will start with discussing the relation between a class of disorder-generated multifractals and logarithmically-correlated random fields and processes. An important example of the latter is provided by the so-called "1/f noise"
From playlist Mathematics

On Furstenberg systems for some aperiodic multiplicative functions - Mariusz Lemanczyk
Special Year Research Seminar Topic: On Furstenberg systems for some aperiodic multiplicative functions Speaker: Mariusz Lemanczyk Affiliation: Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń; Member, School of Mathematics Date: January 17, 2023 The Chowla conjecture from 1965 predicts that all
From playlist Mathematics

Solving a logarithim, log81 (x) = 3/4
👉 Learn how to solve logarithmic equations. Logarithmic equations are equations with logarithms in them. To solve a logarithmic equation, we first isolate the logarithm part of the equation. After we have isolated the logarithm part of the equation, we then get rid of the logarithm. This i
From playlist Solve Logarithmic Equations

Title: Parameterized logarithmic equations and their Galois theory
From playlist Applications of Computer Algebra 2014