
What is the slope of a linear equation
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About
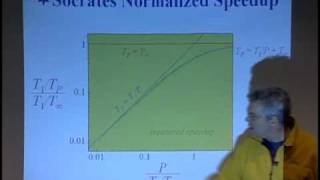
Lec 15 | MIT 6.189 Multicore Programming Primer, IAP 2007
Lecture 15: Cilk (Courtesy of Bradley Kuszmaul and Charles Leiserson. Used with permission.) License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu Subtitles are provided through the generous assistance of Rohan Pai.
From playlist MIT 6.189 Multicore Programming Primer, January (IAP) 2007

Lec 13 | MIT 6.172 Performance Engineering of Software Systems, Fall 2010
Lecture 13: Parallelism and Performance Instructor: Charles Leiserson View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/6-172F10 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT 6.172 Performance Engineering of Software Systems

👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

Lec 22 | MIT 6.046J / 18.410J Introduction to Algorithms (SMA 5503), Fall 2005
Lecture 22: Advanced Topics View the complete course at: http://ocw.mit.edu/6-046JF05 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT 6.046J / 18.410J Introduction to Algorithms (SMA 5503),

The most powerful (and useless) algorithm
0:00 Intro 2:44 The Algorithm 6:38 Why it works 9:28 Code 10:41 Final Thoughts Our implementation of Universal Search: https://github.com/polylog-cs/universal-search/blob/main/code/universal_search.py Impromptu https://impromptu.fun/ More about universal search: -- To prove that the un
From playlist Algorithms
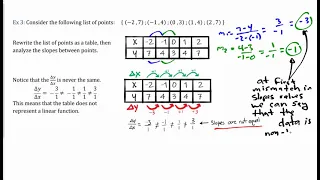
Define linear functions. Use function notation to evaluate linear functions. Learn to identify linear function from data, graphs, and equations.
From playlist Algebra 1

👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About
Ewin Tang - On quantum linear algebra for machine learning - IPAM at UCLA
Recorded 25 January 2022. Ewin Tang of the University of Washington presents "On quantum linear algebra for machine learning" at IPAM's Quantum Numerical Linear Algebra Workshop. Abstract: We will discuss quantum singular value transformation (QSVT), a simple unifying framework for quantum
From playlist Quantum Numerical Linear Algebra - Jan. 24 - 27, 2022

NIPS 2011 Big Learning - Algorithms, Systems, & Tools Workshop: Graphlab 2...
Big Learning Workshop: Algorithms, Systems, and Tools for Learning at Scale at NIPS 2011 Invited Talk: Graphlab 2: The Challenges of Large Scale Computation on Natural Graphs by Carlos Guestrin Carlos Guestrin is an Assistant Professor at Carnegie Mellon's Computer Science and Machine
From playlist NIPS 2011 Big Learning: Algorithms, System & Tools Workshop

Rolando Somma - The Quantum Linear Systems Problem - IPAM at UCLA
Recorded 24 January 2022. Rolando Somma of Los Alamos National Laboratory presents "The Quantum Linear Systems Problem" at IPAM's Quantum Numerical Linear Algebra Workshop. Abstract: The goal of the quantum linear systems problem (QLSP) is to prepare a quantum state proportional to the sol
From playlist Quantum Numerical Linear Algebra - Jan. 24 - 27, 2022

Introduction to Linear Functions and Slope (L10.1)
This lesson introduces linear functions, describes the behavior of linear function, and explains how to determine the slope of a line given two points. Video content created by Jenifer Bohart, William Meacham, Judy Sutor, and Donna Guhse from SCC (CC-BY 4.0)
From playlist Introduction to Functions: Function Basics

Lecture 17, Interpolation | MIT RES.6.007 Signals and Systems, Spring 2011
Lecture 17, Interpolation Instructor: Alan V. Oppenheim View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/RES-6.007S11 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT RES.6.007 Signals and Systems, 1987

What are the x and y intercepts of a linear equation
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

Define a linear function. Determine if a linear function is increasing or decreasing. Interpret linear function models. Determine linear functions. Site: http://mathispower4u.com
From playlist Introduction to Functions: Function Basics

What is the parent function of a linear graph
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

What do I need to know to graph an equation in slope intercept form
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

Machine learning techniques in quantum information (...) - A. Rocchetto - Workshop 1 - CEB T2 2018
Andrea Rocchetto (University of Oxford and UCL) / 15.05.2018 Machine learning techniques in quantum information theory: a selection of results During this talk I will present a selection of results at the intersection of quantum information, quantum computation, and machine learning. Fir
From playlist 2018 - T2 - Measurement and Control of Quantum Systems: Theory and Experiments
