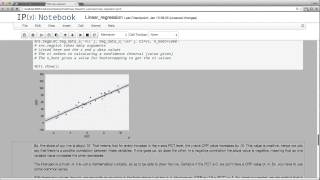
Linear regression is used to compare sets or pairs of numerical data points. We use it to find a correlation between variables.
From playlist Learning medical statistics with python and Jupyter notebooks

👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

What is the parent function of a linear graph
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

What is the slope of a linear equation
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

Summary for graph an equation in Standard form
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

What is everything you need to know to graph an equation in slope intercept form
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About
Introduction to R: Linear Regression
This lesson covers the basics of linear regression in R. It includes a discussion of basic linear regression, polynomial regression and multiple linear regression as well as some assumptions and potential sources of problems when making linear regression models. This is lesson 27 of a 30-
From playlist Introduction to R

Python for Data Analysis: Linear Regression
This video covers the basics of linear regression and how to perform linear regression in Python. Subscribe: ► https://www.youtube.com/c/DataDaft?sub_confirmation=1 This is lesson 27 of a 30-part introduction to the Python programming language for data analysis and predictive modeling. L
From playlist Python for Data Analysis

What do I need to know to graph an equation in slope intercept form
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

Linear Regression in R | Linear Regression in R With Example | Data Science Algorithms | Simplilearn
This Linear regression in R video will help you understand what is linear regression, why linear regression, and linear regression in R with example. You will also look at a use case predicting the revenue of a company using multiple linear regression. Now, let's deep dive into this video
From playlist Data Science For Beginners | Data Science Tutorial🔥[2022 Updated]

Fundamental Machine Learning Algorithms - Linear Regression
The code is accessible at https://github.com/sepinouda/Machine-Learning/
From playlist Machine Learning Course

Average Treatment Effects: Confounding
Professor Stefan Wager on confounding and regression adjustments. Comparison of regression adjustments done via OLS versus generic machine learning.
From playlist Machine Learning & Causal Inference: A Short Course

Linear Regression Analysis | Linear Regression in Python | Machine Learning Algorithms | Simplilearn
🔥 Advanced Certificate Program In Data Science: https://www.simplilearn.com/pgp-data-science-certification-bootcamp-program?utm_campaign=MachineLearning-NUXdtN1W1FE&utm_medium=Descriptionff&utm_source=youtube 🔥 Data Science Bootcamp (US Only): https://www.simplilearn.com/data-science-bootc
From playlist Machine Learning with Python | Complete Machine Learning Tutorial | Simplilearn [2022 Updated]

Data Analysis 9: Data Regression - Computerphile
Real life doesn't fit into neat categories - Dr Mike Pound on some different ways to regress your data. This is part 9 of the Data Analysis Learning Playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLzH6n4zXuckpfMu_4Ff8E7Z1behQks5ba This Learning Playlist was designed by Dr Mercedes Torr
From playlist Data Analysis with Dr Mike Pound

Linear Regression - r and r-squared
I recently uploaded 200 videos that are much more concise with excellent graphics. Click the link in the upper right-hand corner of this video. It will take you to my youtube channel where videos are arranged in playlists. In this older video: Must see video that explains r and r-squared
From playlist Unit 3: Linear and Non-Linear Regression

JASP - Simple Linear Regression
Lecturer: Dr. Erin M. Buchanan Spring 2020 Simple linear regression is an extension of correlation - but also learn about how to understand and interpret multiple linear regression, the regression assumptions, and more! Learn more and find our documents on our OSF page: https://osf.io/t5
From playlist Learn JASP + Statistics

What are the x and y intercepts of a linear equation
👉 Learn about graphing linear equations. A linear equation is an equation whose highest exponent on its variable(s) is 1. i.e. linear equations has no exponents on their variables. The graph of a linear equation is a straight line. To graph a linear equation, we identify two values (x-valu
From playlist ⚡️Graph Linear Equations | Learn About

Applied Machine Learning: Secret Sauce
Professor Jann Spiess shares the secret sauce of applied machine learning.
From playlist Machine Learning & Causal Inference: A Short Course