Optimal control | Search algorithms
Linear-quadratic regulator rapidly-exploring random tree
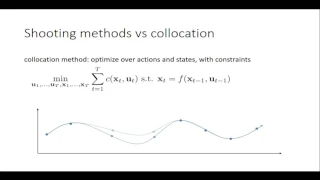
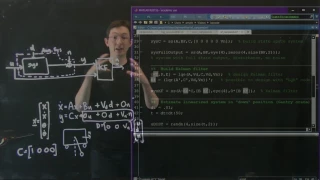
Linear-quadratic regulator rapidly-exploring random tree (LQR-RRT) is a sampling based algorithm for kinodynamic planning. A solver is producing random actions which are forming a funnel in the state space. The generated tree is the action sequence which fulfills the cost function. The restriction is, that a prediction model, based on differential equations, is available to simulate a physical system. (Wikipedia).