
Solving an Absolute Value Equation
Lean how to solve absolute value equations. Absolute value of a number is the positive value of the number. For instance, the absolute value of 2 is 2 and the absolute value of -2 is also 2. To solve an absolute value equations we need to create the two cases: the positive case and the neg
From playlist Solve Absolute Value Equations

http://mathispower4u.wordpress.com/
From playlist Solving Absolute Value Equations

Hankel Alternative View of Koopman (HAVOK) Analysis [SHORT]
This video illustrates a new algorithm to decompose chaos into a linear system with intermittent forcing. This is based on the Hankel Alternative View of Koopman (HAVOK) analysis that builds linear regression models on eigen-time-delay coordinates. Chaos as an Intermittently Forced Line
From playlist Research Abstracts from Brunton Lab

What is the definition of absolute value
http://www.freemathvideos.com In this video playlist you will learn how to solve and graph absolute value equations and inequalities. When working with absolute value equations and functions it is important to understand that the absolute value symbol represents the absolute distance from
From playlist Solve Absolute Value Equations

Data-Driven Control: Eigensystem Realization Algorithm Procedure
In this lecture, we describe the eigensystem realization algorithm (ERA) in detail, including step-by-step algorithmic instructions. https://www.eigensteve.com/
From playlist Data-Driven Control with Machine Learning

Data-Driven Control: Balanced Proper Orthogonal Decomposition
In this lecture, we introduce the balancing proper orthogonal decomposition (BPOD) to approximate balanced truncation for high-dimensional systems. https://www.eigensteve.com/
From playlist Data-Driven Control with Machine Learning

Peter Benner: Matrix Equations and Model Reduction, Lecture 4
Peter Benner from the Max Planck Institute presents: Matrix Equations and Model Reduction; Lecture 4
From playlist Gene Golub SIAM Summer School Videos

Data-Driven Control: Balanced Truncation and BPOD Example
In this lecture, we explore balanced truncation and BPOD on a numerical example in Matlab. Code: faculty.washington.edu/sbrunton/DataDrivenControl.zip https://www.eigensteve.com/
From playlist Data-Driven Control with Machine Learning

Alexander Pushnitski : Rational approximation of functions with logarithmic singularities
Find this video and other talks given by worldwide mathematicians on CIRM's Audiovisual Mathematics Library: http://library.cirm-math.fr. And discover all its functionalities: - Chapter markers and keywords to watch the parts of your choice in the video - Videos enriched with abstracts, b
From playlist Analysis and its Applications

Hankel Alternative View of Koopman (HAVOK) Analysis [FULL]
This video illustrates a new algorithm to decompose chaos into a linear system with intermittent forcing. This is based on the Hankel Alternative View of Koopman (HAVOK) analysis that builds linear regression models on eigen-time-delay coordinates. Chaos as an Intermittently Forced Line
From playlist Research Abstracts from Brunton Lab
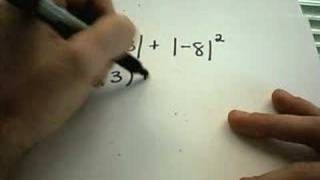
Absolute Value and Evaluating Numbers
Thanks to all of you who support me on Patreon. You da real mvps! $1 per month helps!! :) https://www.patreon.com/patrickjmt !! Absolute Value and Evaluating Numbers - Numerous numerical examples are shown! For more free math videos, visit http://PatrickJMT.com
From playlist Absolute Value
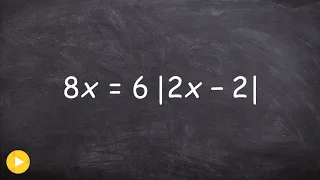
Solving a multi step absolute value equation
Learn how to solve absolute value equations with extraneous solutions. Absolute value of a number is the positive value of the number. For instance, the absolute value of 2 is 2 and the absolute value of -2 is also 2. To solve an absolute value problem, we first isolate the absolute value
From playlist Solve Absolute Value Equations

Graphing Absolute Value Function & Solving Related Inequality
More resources available at www.misterwootube.com
From playlist Further Work with Functions

Solving a One Step Absolute Value Equation
Lean how to solve absolute value equations. Absolute value of a number is the positive value of the number. For instance, the absolute value of 2 is 2 and the absolute value of -2 is also 2. To solve an absolute value equations we need to create the two cases: the positive case and the neg
From playlist Solve Absolute Value Equations

Necmiye Ozay: "A fresh look at some classical system identification methods"
Intersections between Control, Learning and Optimization 2020 "A fresh look at some classical system identification methods" Necmiye Ozay - University of Michigan Abstract: System identification has a long history with several well-established methods, in particular for learning linear d
From playlist Intersections between Control, Learning and Optimization 2020

Data-Driven Control: Error Bounds for Balanced Truncation
In this lecture, we derive error bounds for the balanced truncation. https://www.eigensteve.com/
From playlist Data-Driven Control with Machine Learning

How To Solve an Absolute Value Equation and Test Our Solutions when They Do Not Work
Learn how to solve absolute value equations with extraneous solutions. Absolute value of a number is the positive value of the number. For instance, the absolute value of 2 is 2 and the absolute value of -2 is also 2. To solve an absolute value problem, we first isolate the absolute value
From playlist Solve Absolute Value Equations

Patrick Gerard: Singular value dynamics and nonlinear Fourier transform for Hankel operators on the
The lecture was held within the framework of the Hausdorff Trimester Program Harmonic Analysis and Partial Differential Equations. 14.7.2014
From playlist HIM Lectures: Trimester Program "Harmonic Analysis and Partial Differential Equations"

Solving an Absolute Value Equation and Checking for Extraneous Solutions
Learn how to solve absolute value equations with extraneous solutions. Absolute value of a number is the positive value of the number. For instance, the absolute value of 2 is 2 and the absolute value of -2 is also 2. To solve an absolute value problem, we first isolate the absolute value
From playlist Solve Absolute Value Equations
