
GCSE Science Revision "Systematic Errors"
In this video, we look at systematic errors. First we explore what is meant by a systematic error. We then look at what can cause a systematic error, including a zero error. Image Credits Thermometer https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Laboratory_thermometer-03.jpg Lilly_M, CC BY-SA
From playlist GCSE Working Scientifically

Teach Astronomy - Random and Systematic Errors
http://www.teachastronomy.com/ In science we deal with two fundamentally different types of errors. Random errors are usually associated with limitations in the measuring apparatus. A random error can displace a measurement either to the high or low side of the true value. Random errors
From playlist 01. Fundamentals of Science and Astronomy

Comparison of systematic and random error. Types of systematic error, including offset error and scale factor error/
From playlist Experimental Design
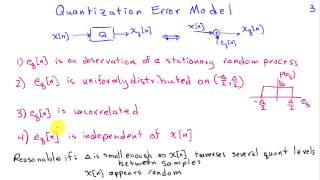
Analysis of Quantization Error
http://AllSignalProcessing.com for more great signal processing content, including concept/screenshot files, quizzes, MATLAB and data files. Modeling quantization error as uncorrelated noise. Signal to quantization noise ratio as a function of the number of bits used to represent the sign
From playlist Sampling and Reconstruction of Signals

What Are Error Intervals? GCSE Maths Revision
What are error Intervals and how do we find them - that's the mission in this episode of GCSE Maths minis! Error Intervals appear on both foundation and higher tier GCSE maths and IGCSE maths exam papers, so this is excellent revision for everyone! DOWNLOAD THE QUESTIONS HERE: https://d
From playlist Error Intervals & Bounds GCSE Maths Revision

How To Identify Type I and Type II Errors In Statistics
This statistics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into Type I errors and Type II errors. A type I error occurs when a true null hypothesis is rejected. A type II error occurs when a false null hypothesis is not rejected. This video contains a few examples and practice problem
From playlist Statistics
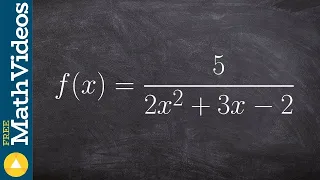
Learn how to find and classify the discontinuity of the function
👉 Learn how to classify the discontinuity of a function. A function is said to be discontinuous if there is a gap in the graph of the function. Some discontinuities are removable while others are non-removable. There is also jump discontinuity. A discontinuity is removable when the denomi
From playlist Holes and Asymptotes of Rational Functions

Random and systematic error explained: from fizzics.org
In scientific experiments and measurement it is almost never possible to be absolutely accurate. We tend to make two types of error, these are either random or systematic. The video uses examples to explain the difference and the first steps you might take to reduce them. Notes to support
From playlist Units of measurement

Dong An - Improved complexity estimation for Hamiltonian simulation with Trotter formula
Recorded 25 January 2022. Dong An of the University of Maryland presents "Improved complexity estimation for Hamiltonian simulation with Trotter formula" at IPAM's Quantum Numerical Linear Algebra Workshop. Abstract: Trotter formula is one of the most widely used methods for time-dependent
From playlist Quantum Numerical Linear Algebra - Jan. 24 - 27, 2022

Raúl Tempone: Adaptive strategies for Multilevel Monte Carlo
Abstract: We will first recall, for a general audience, the use of Monte Carlo and Multi-level Monte Carlo methods in the context of Uncertainty Quantification. Then we will discuss the recently developed Adaptive Multilevel Monte Carlo (MLMC) Methods for (i) It Stochastic Differential Equ
From playlist Probability and Statistics

Mod-01 Lec-31 Initial Value Problem
Elementary Numerical Analysis by Prof. Rekha P. Kulkarni,Department of Mathematics,IIT Bombay.For more details on NPTEL visit http://nptel.ac.in
From playlist NPTEL: Elementary Numerical Analysis | CosmoLearning Mathematics

Plamen Turkedjiev: Least squares regression Monte Carlo for approximating BSDES and semilinear PDES
Abstract: In this lecture, we shall discuss the key steps involved in the use of least squares regression for approximating the solution to BSDEs. This includes how to obtain explicit error estimates, and how these error estimates can be used to tune the parameters of the numerical scheme
From playlist Probability and Statistics
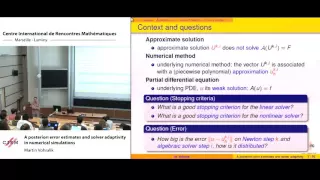
Martin Vohralik: A posteriori error estimates and solver adaptivity in numerical simulations
Abstract: We review how to bound the error between the unknown weak solution of a PDE and its numerical approximation via a fully computable a posteriori estimate. We focus on approximations obtained at an arbitrary step of a linearization (Newton-Raphson, fixed point, ...) and algebraic s
From playlist Numerical Analysis and Scientific Computing

Benjamin Stamm - Eigenvalue problems and error control - IPAM at UCLA
Recorded 10 March 2022. Benjamin Stamm of RWTH Aachen University presents "Eigenvalue problems and error control" at IPAM's Advancing Quantum Mechanics with Mathematics and Statistics Tutorials. Learn more online at: http://www.ipam.ucla.edu/programs/workshops/advancing-quantum-mechanics-w
From playlist Tutorials: Advancing Quantum Mechanics with Mathematics and Statistics - March 8-11, 2022

On the numerical integration of the Lorenz-96 model... - Grudzien - Workshop 2 - CEB T3 2019
Grudzien (U Nevada in Reno, USA) / 13.11.2019 On the numerical integration of the Lorenz-96 model, with scalar additive noise, for benchmark twin experiments ---------------------------------- Vous pouvez nous rejoindre sur les réseaux sociaux pour suivre nos actualités. Facebook
From playlist 2019 - T3 - The Mathematics of Climate and the Environment

Imaging with Unstructured Adaptive Meshes
37th Imaging & Inverse Problems (IMAGINE) OneWorld SIAM-IS Virtual Seminar Series Talk Date: February 2, 10:00am Eastern Time Zone (US & Canada) / 2:00pm GMT Speaker: Erkki Somersalo, Case Western Reserve University Abstract: In many applications, imaging problems involve a numerical solu
From playlist Imaging & Inverse Problems (IMAGINE) OneWorld SIAM-IS Virtual Seminar Series

FFT based spectral Ewald methods as an alternative to multipole methods – A.-K. Tornberg – ICM2018
Numerical Analysis and Scientific Computing Invited Lecture 15.5 FFT based spectral Ewald methods as an alternative to fast multipole methods Anna-Karin Tornberg Abstract: In this paper, we review a set of fast and spectrally accurate methods for rapid evaluation of three dimensional ele
From playlist Numerical Analysis and Scientific Computing
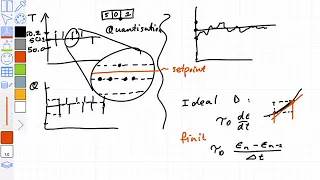
Practical control issues Lecture 2019-02-13
Discretisation and quantisation error, discrete PI and code.
From playlist CPB Theme 1

GCSE Science Revision "Random Errors"
In this video, we look at random errors. First we explore what is meant by random errors and look at examples of how they occur. We then explore how we can reduce the effects of random errors. Image Credits Thermometer https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Laboratory_thermometer-03.jpg
From playlist GCSE Working Scientifically
