Euclidean solid geometry | Angle
Dihedral angle
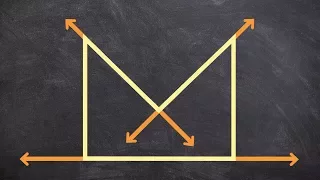
A dihedral angle is the angle between two intersecting planes or half-planes. In chemistry, it is the clockwise angle between half-planes through two sets of three atoms, having two atoms in common. In solid geometry, it is defined as the union of a line and two half-planes that have this line as a common edge. In higher dimensions, a dihedral angle represents the angle between two hyperplanes.The planes of a flying machine are said to be at positive dihedral angle when both starboard and port main planes (commonly called wings) are upwardly inclined to the lateral axis. When downwardly inclined they are said to be at a negative dihedral angle. (Wikipedia).