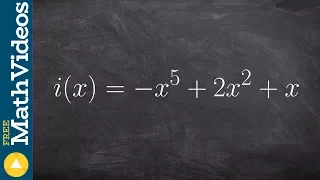Hidden oscillation | Nonlinear control
Describing function
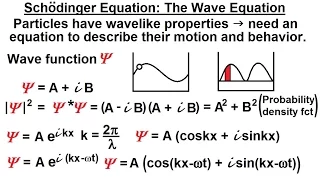
In control systems theory, the describing function (DF) method, developed by Nikolay Mitrofanovich Krylov and Nikolay Bogoliubov in the 1930s, and extended by Ralph Kochenburger is an approximate procedure for analyzing certain nonlinear control problems. It is based on quasi-linearization, which is the approximation of the non-linear system under investigation by a linear time-invariant (LTI) transfer function that depends on the amplitude of the input waveform. By definition, a transfer function of a true LTI system cannot depend on the amplitude of the input function because an LTI system is linear. Thus, this dependence on amplitude generates a family of linear systems that are combined in an attempt to capture salient features of the non-linear system behavior. The describing function is one of the few widely applicable methods for designing nonlinear systems, and is very widely used as a standard mathematical tool for analyzing limit cycles in closed-loop controllers, such as industrial process controls, servomechanisms, and electronic oscillators. (Wikipedia).