
0/1 Knapsack problem | Dynamic Programming
Overview of the 0/1 Knapsack problem using dynamic programming Algorithms repository: https://github.com/williamfiset/algorithms My website: http://www.williamfiset.com
From playlist Dynamic Programming

0-1 Knapsack Problem (Dynamic Programming)
Dynamic Programming Tutorial with 0-1 Knapsack Problem
From playlist Dynamic Programming Tutorial Series

Knapsack Problem Using Dynamic Programming | 0/1 Knapsack Problem | Data Structures | Simplilearn
This video on knapsack Problem Using Dynamic Programming will acquaint you with a clear understanding of the fractional or 0-1 knapsack problem statement and solution implementation. In this Data Structure Tutorial, you will understand why the difference between 0-1 knapsack and fractional
From playlist Data Structures & Algorithms

Math for Liberal Studies - Lecture 1.9 The Knapsack Problem
This video covers material from Math for Liberal Studies Section 1.9: The Knapsack Problem. In this video, I explain what the knapsack problem is, and we work through an example using a recursive algorithm to solve the problem.
From playlist Math for Liberal Studies Lectures
Dynamic Programming 1 [Programming Competition Problems]
Source code: http://problemvault.com/index.php#problem127 Problem source / Online judge: https://open.kattis.com/problems/knapsack This video explores a classic dynamic programming problem known as the "0/1 Knapsack Problem". We walk through how the algorithm works, then we go ahead and i
From playlist Programming Competition Problems with Micah Stairs

What is the quantum measurement problem?
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel for all the latest from World Science U. Visit our Website: http://www.worldscienceu.com/ Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/worldscienceu Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/worldscienceu
From playlist Science Unplugged: Quantum Mechanics
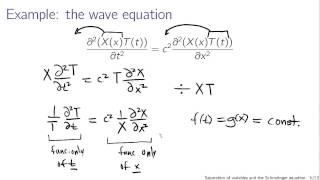
Separation of variables and the Schrodinger equation
A brief explanation of separation of variables, application to the time-dependent Schrodinger equation, and the solution to the time part. (This lecture is part of a series for a course based on Griffiths' Introduction to Quantum Mechanics. The Full playlist is at http://www.youtube.com/
From playlist Mathematical Physics II - Youtube

Turing Machines and The Halting Problem (Part 2)
The Halting Problem has fascinated thousands of computer scientists from around the world. A major part of Computing Logic, the proof of the halting problem proves that computers can't do everything. Check out the video to learn more about why computers work the way they do! For Turing Ma
From playlist Math

1. Introduction, Optimization Problems (MIT 6.0002 Intro to Computational Thinking and Data Science)
MIT 6.0002 Introduction to Computational Thinking and Data Science, Fall 2016 View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/6-0002F16 Instructor: John Guttag Prof. Guttag provides an overview of the course and discusses how we use computational models to understand the world in which we li
From playlist MIT 6.0002 Introduction to Computational Thinking and Data Science, Fall 2016

Knapsack, Bandwidth Min. Intro: Greedy Algorithms - Lecture 14
All rights reserved for http://www.aduni.org/ Published under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike license http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/ Tutorials by Instructor: Shai Simonson. http://www.stonehill.edu/compsci/shai.htm Visit the forum at: http://www.coderisland.c
From playlist ArsDigita Algorithms by Shai Simonson

Heiko Röglin: Smoothed Analysis of Algorithms (Part 2)
The lecture was held within the framework of the Hausdorff Trimester Program: Combinatorial Optimization
From playlist HIM Lectures 2015

Lec 18 | MIT 6.00SC Introduction to Computer Science and Programming, Spring 2011
Lecture 18: Optimization Problems and Algorithms Instructor: John Guttag View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/6-00SCS11 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
From playlist MIT 6.00SC Introduction to Computer Science and Programming

Dynamic Programming Crash Course | Advanced Data Structures And Algorithms Tutorial | Simplilearn
🔥Post Graduate Program In Full Stack Web Development: https://www.simplilearn.com/pgp-full-stack-web-development-certification-training-course?utm_campaign=DynamicProgrammingCrashCourse-xZKqH7ZcS_Y&utm_medium=DescriptionFF&utm_source=youtube 🔥Caltech Coding Bootcamp (US Only): https://www.
From playlist Data Structures & Algorithms [2022 Updated]

Robert Weismantel: Affine TU decomposition of matrices
We study the reformulation of integer linear programs by means of a mixed integer linear program with fewer integer variables. Such reformulations can be solved efficiently with mixed integer linear programming techniques. We exhibit a variety of examples that demonstrate how integer prog
From playlist HIM Lectures: Trimester Program "Combinatorial Optimization"

Lec 12 | MIT 6.00 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming, Fall 2008
Lecture 12: More about debugging, knapsack problem, introduction to dynamic programming Instructors: Prof. Eric Grimson, Prof. John Guttag View the complete course at: http://ocw.mit.edu/6-00F08 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms Mor
From playlist MIT 6.00 Intro to Computer Science & Programming, Fall 2008

If You Don't Understand Quantum Physics, Try This!
A simple and clear explanation of all the important features of quantum physics that you need to know. Check out this video's sponsor https://brilliant.org/dos I have spent a lot of time thinking about how best to explain quantum physics and this is the result of all my hours of pondering
From playlist The Map of Quantum Physics Expanded

Why do physicists try to understand time?
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel for all the latest from World Science U. Visit our Website: http://www.worldscienceu.com/ Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/worldscienceu Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/worldscienceu
From playlist Science Unplugged: Time

Lec 14 | MIT 6.00 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming, Fall 2008
Lecture 14: Analysis of knapsack problem, introduction to object-oriented programming Instructors: Prof. Eric Grimson, Prof. John Guttag View the complete course at: http://ocw.mit.edu/6-00F08 License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms More courses at
From playlist MIT 6.00 Intro to Computer Science & Programming, Fall 2008