
How to find correlation in Excel with the Data Analysis Toolpak
Click this link for more information on correlation coefficients plus more FREE Excel videos and tips: http://www.statisticshowto.com/what-is-the-pearson-correlation-coefficient/
From playlist Regression Analysis

Scatterplots, Part 3: The Formula Behind the Correlation Coefficient
We use the Scatterplots & Correlation app to explain the formula behind the correlation coefficient. The app allows you to find and plot the z-scores, showing the 4 quadrants in which points on the scatterplot can fall.
From playlist Chapter 3: Relationships between two variables

Estimate the Correlation Coefficient Given a Scatter Plot
This video explains how to estimate the correlation coefficient given a scatter plot.
From playlist Performing Linear Regression and Correlation

Graphing Equations By Plotting Points - Part 2
This video shows how to graph equations by plotting points. Part 2 of 2 http://www.mathispower4u.yolasite.com
From playlist Graphing Various Functions

Graphing Equations By Plotting Points - Part 1
This video shows how to graph equations by plotting points. Part 1 of 2 http://www.mathispower4u.yolasite.com
From playlist Graphing Various Functions

What are the key points to trigonometric graphs
👉 Learn the basics of graphing trigonometric functions. The graphs of trigonometric functions are cyclical graphs which repeats itself for every period. To graph the parent graph of a trigonometric function, we first identify the critical points which includes: the x-intercepts, the maximu
From playlist How to Graph Trigonometric Functions

Phase shifts of trigonometric functions
👉 Learn the basics of graphing trigonometric functions. The graphs of trigonometric functions are cyclical graphs which repeats itself for every period. To graph the parent graph of a trigonometric function, we first identify the critical points which includes: the x-intercepts, the maximu
From playlist How to Graph Trigonometric Functions

Speech and Audio Processing 4: Speech Coding I - Professor E. Ambikairajah
Speech and Audio Processing Speech Coding - Lecture notes available from: http://eemedia.ee.unsw.edu.au/contents/elec9344/LectureNotes/
From playlist ELEC9344 Speech and Audio Processing by Prof. Ambikairajah

Using composition of inverses using triangles
👉 Learn how to evaluate an expression with the composition of a function and a function inverse. Just like every other mathematical operation, when given a composition of a trigonometric function and an inverse trigonometric function, you first evaluate the one inside the parenthesis. We
From playlist Evaluate a Composition of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
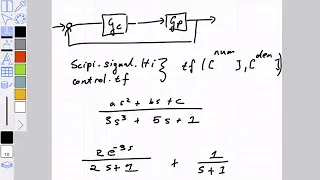
Simulation of systems with dead time Lecture 2019-02-27
Systems with dead time make it hard to do closed loop simulations. I cover a couple of ways to handle this. The video showing only the closed loop simulation of a loop in Modelica is here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dw66ODbMS2A
From playlist Simulation

2017 #2 Free Response Question - AP Physics 1 - Exam Solution
My solutions to Free Response Question #2 from the 2017 AP Physics 1 Exam. Also included are my reflections on how to get more points on the exam. Want Lecture Notes? http://www.flippingphysics.com/ap1-2017-frq2.html This Experimental Design question also works as a part of the AP Physics
From playlist AP Physics 1 - EVERYTHING!!

Continuous descriptions for dry active matter by Eric Bertin
Discussion Meeting: Nonlinear Physics of Disordered Systems: From Amorphous Solids to Complex Flows URL: http://www.icts.res.in/discussion_meeting/NPDS2015/ Dates: Monday 06 Apr, 2015 - Wednesday 08 Apr, 2015 Description: In recent years significant progress has been made in the physics
From playlist Discussion Meeting: Nonlinear Physics of Disordered Systems: From Amorphous Solids to Complex Flows
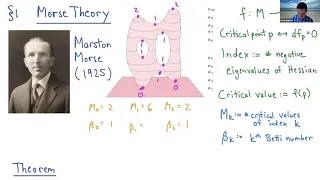
Peter Bubenik - Lecture 1 - TDA: Summaries and Distances
38th Annual Geometric Topology Workshop (Online), June 15-17, 2021 Peter Bubenik, University of Florida Title: TDA: Summaries and Distances Abstract: Topological Data Analysis (TDA) uses tools based on topology to address challenges in data science. In these talks I will focus on the part
From playlist 38th Annual Geometric Topology Workshop (Online), June 15-17, 2021
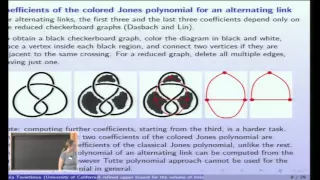
A refined upper bound for the volume...Jones polynomial - Anastasiia Tsvietkova
Anastasiia Tsvietkova, UC Davis October 8, 2015 http://www.math.ias.edu/wgso3m/agenda 2015-2016 Monday, October 5, 2015 - 08:00 to Friday, October 9, 2015 - 12:00 This workshop is part of the topical program "Geometric Structures on 3-Manifolds" which will take place during the 2015-2016
From playlist Workshop on Geometric Structures on 3-Manifolds

Lecture 16: Microarray Disease Classification II
MIT HST.512 Genomic Medicine, Spring 2004 Instructor: Dr. Steven A. Greenberg View the complete course: https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/hst-512-genomic-medicine-spring-2004/ YouTube Playlist: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_-gQchCLmXk&list=PLUl4u3cNGP613PJMNmRjAIdBr76goU1V5 I thought what w
From playlist MIT HST.512 Genomic Medicine, Spring 2004

Complex Numbers Exam Review (3 of 4: Cube roots of unity)
More resources available at www.misterwootube.com
From playlist Using Complex Numbers

Huyên Pham - Randomization approach for stochastic control problems
Huyên Pham (Université Paris Diderot) We study optimal stochastic control problem for non-Markovian stochastic differential equations (SDEs) where the drift, diffusion coefficients, and gain functionals are path-dependent, and importantly we do not make any ellipticity assumption on the
From playlist Schlumberger workshop on Topics in Applied Probability
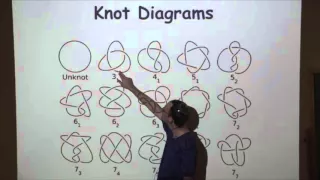
CSDM - Chaim Even Zohar - October 6, 2015
http://www.math.ias.edu/calendar/event/83624/1444141800/1444149000
From playlist Computer Science/Discrete Mathematics

What is the amplitude of a trigonometric graph
👉 Learn the basics of graphing trigonometric functions. The graphs of trigonometric functions are cyclical graphs which repeats itself for every period. To graph the parent graph of a trigonometric function, we first identify the critical points which includes: the x-intercepts, the maximu
From playlist How to Graph Trigonometric Functions
